Protocol for the Weight-bearing in Ankle Fractures (WAX) trial: a multicentre prospective non-inferiority trial of early versus delayed weight-bearing after operatively managed ankle fracture, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
By A Mystery Man Writer
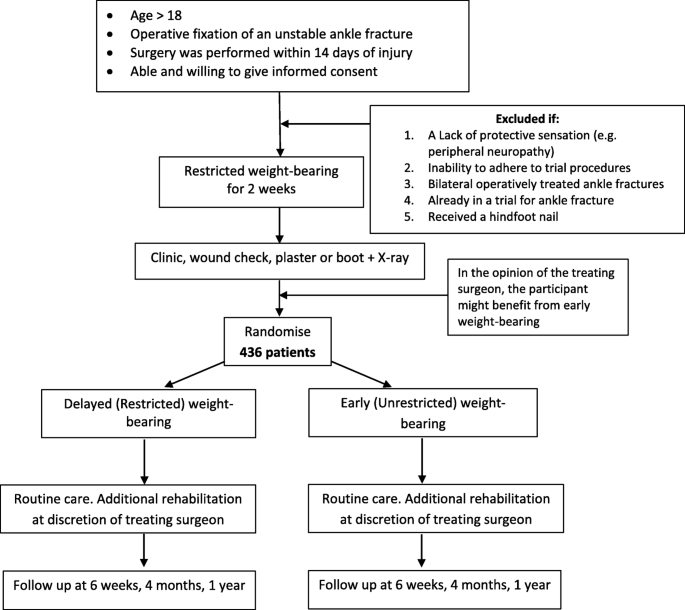
Background Unstable ankle fractures represent a substantial burden of disease, accounting for a mean hospital stay of nine days, a mean cost of £4,491 per patient and 20,000 operations per year. There is variation in UK practice around weight-bearing instructions after operatively managed ankle fracture. Early weight-bearing may reduce reliance on health services, time off work, and improve functional outcomes. However, concerns remain about the potential for complications such as implant failure. This is the protocol of a multicentre randomised non-inferiority clinical trial of weight-bearing following operatively treated ankle fracture. Methods Adults aged 18 years and over who have been managed operatively for ankle fracture will be assessed for eligibility. Baseline function (Olerud and Molander Ankle Score [OMAS]), health-related quality of life (EQ-5D-5L), and complications will be collected after informed consent has been obtained. A randomisation sequence has been prepared by a trial statistician to allow for 1:1 allocation to receive either instruction to weight-bear as pain allows from the point of randomisation, two weeks after the time of surgery (‘early weight-bearing’ group) or to not weight-bear for a further four weeks (‘delayed weight -bearing’ group). All other treatment will be as per the guidance of the treating clinician. Participants will be asked about their weight-bearing status weekly until four weeks post-randomisation. At four weeks post-randomisation complications will be collected. At six weeks, four months, and 12 months post-randomisation, the OMAS, EQ-5D-5L, complications, physiotherapy input, and resource use will be collected. The primary outcome measure is ankle function (OMAS) at four months post-randomisation. A minimum of 436 participants will be recruited to obtain 80% power to detect a non-inferiority margin of -6 points on the OMAS 4 months post-randomisation. A within-trial health economic evaluation will be conducted to estimate the cost-effectiveness of the treatment options. Discussion The results of this study will inform national guidance with regards to the most clinically and cost-effective strategy for weight-bearing after surgery for unstable ankle fractures. Trial registration ISRCTN12883981 , Registered 02 December 2019.

Functional bracing is a safe and cost effective treatment for isolated Weber B fracture - ScienceDirect

Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine - A protocol for permissive weight- bearing during allied health therapy in surgically treated fractures of the pelvis and lower extremities - HTML
Prospective randomized controlled trial: early weight bearing after conservative treatment of Weber B ankle fractures (pancake trial)
Impact of Joint Laxity Before Total Knee Arthroplasty on Postoperative Ligament Balance
Weight bearing or non-weight bearing after surgically fixed ankle fractures, the WOW! Study: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Weight-Bearing and Mobilization in the Postoperative Care of Ankle Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies

A Stability-Based Management Protocol for Isolated Lateral Malleolar Ankle Fractures at the Level of the Syndesmosis Reduces the Need for Surgical Intervention

Weight-bearing in ankle fractures: An audit of UK practice - ScienceDirect

Fractures of the lateral malleolus – a retrospective before-and-after study of treatment and resource utilization following the implementation of a structured treatment algorithm, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders

Ankle fracture management
- Chantelle Seamless Soft Stretch Brief Panty 3-Pack

- TRASA Women's Maternity Cotton Leggings Pregnancy Yoga Pants with Pock –

- Dan Shapiro - Manière De Voir
- Classic Style Underwire Lightly Padded Bra & Panty Set. I DLY

- Cheap White Textured Ceramic Floor Tiles Manufacturers and Suppliers - Wholesale Price White Textured Ceramic Floor Tiles - HANSE






