Alveolar macrophages help CD8+ T cells go (anti-)viral

By A Mystery Man Writer
The human immune system is a highly complex network of cells, signals, and responses that is tightly regulated to ensure that the body can fight off infection without damaging its own tissues. Now, researchers from Japan report a new way in which the immune system protects lung tissue from viral infections.
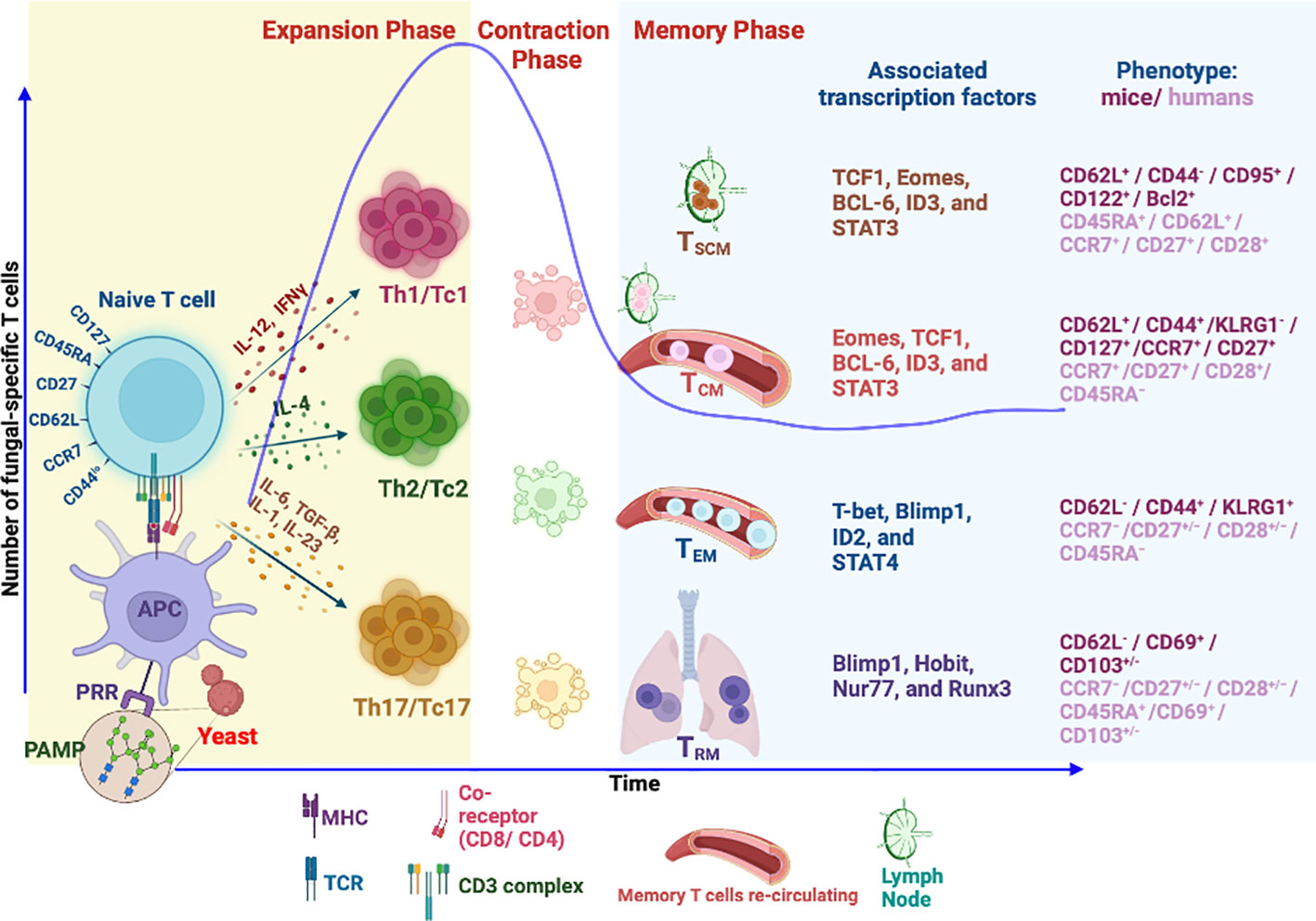
Frontiers T cell responses to control fungal infection in an immunological memory lens
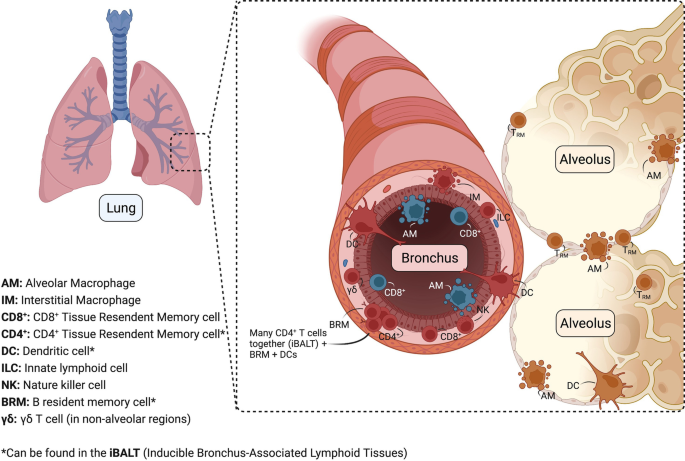
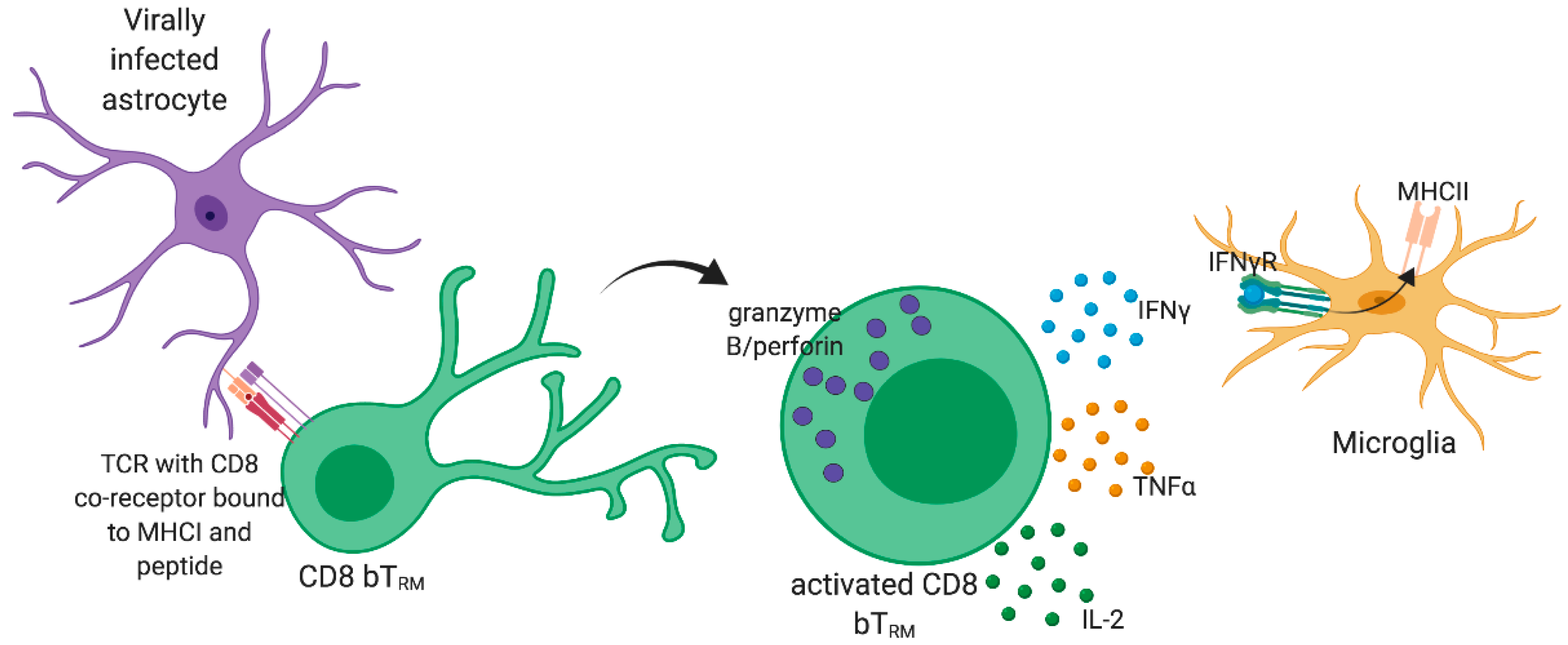
Tissue-resident immunity in the lung: a first-line defense at the environmental interface
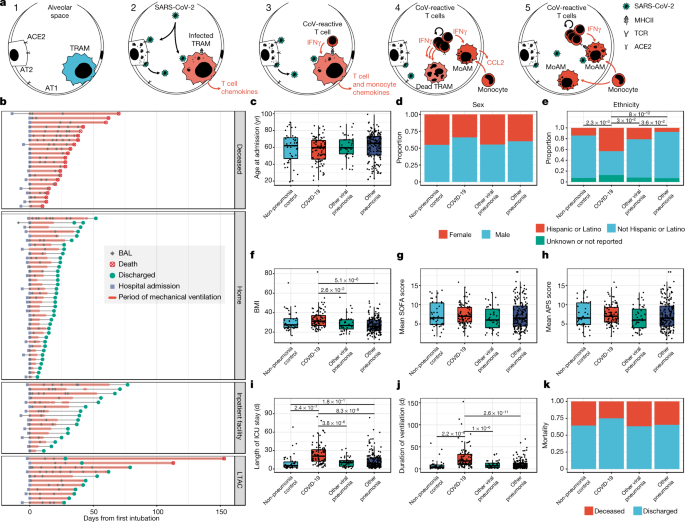
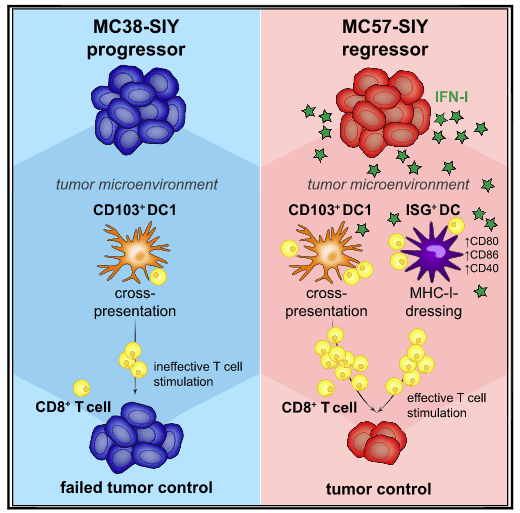
Circuits between infected macrophages and T cells in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia

Research outcomes
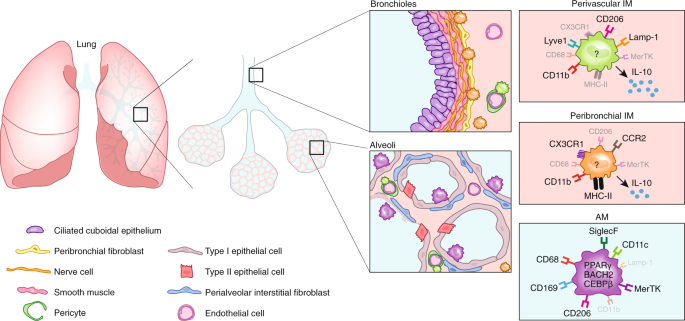
Does tissue imprinting restrict macrophage plasticity?
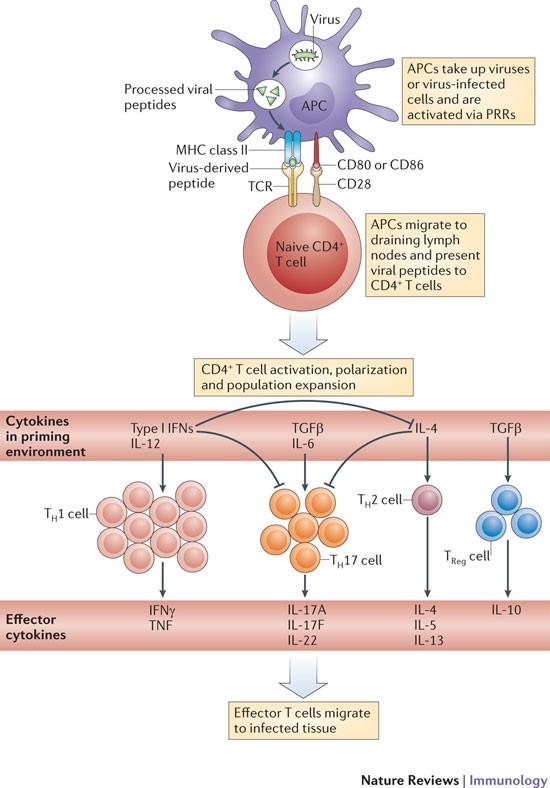
Expanding roles for CD4+ T cells in immunity to viruses
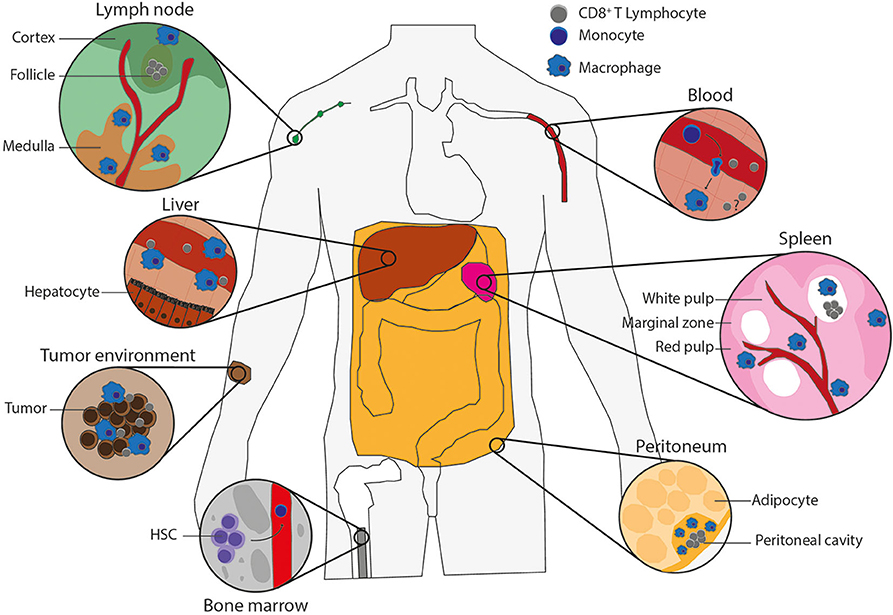
Frontiers Antigen Cross-Presentation by Macrophages

In vivo CD8+ T cell CRISPR screening reveals control by Fli1 in infection and cancer - ScienceDirect

Glutaminase inhibition impairs CD8 T cell activation in STK11-/Lkb1-deficient lung cancer - ScienceDirect
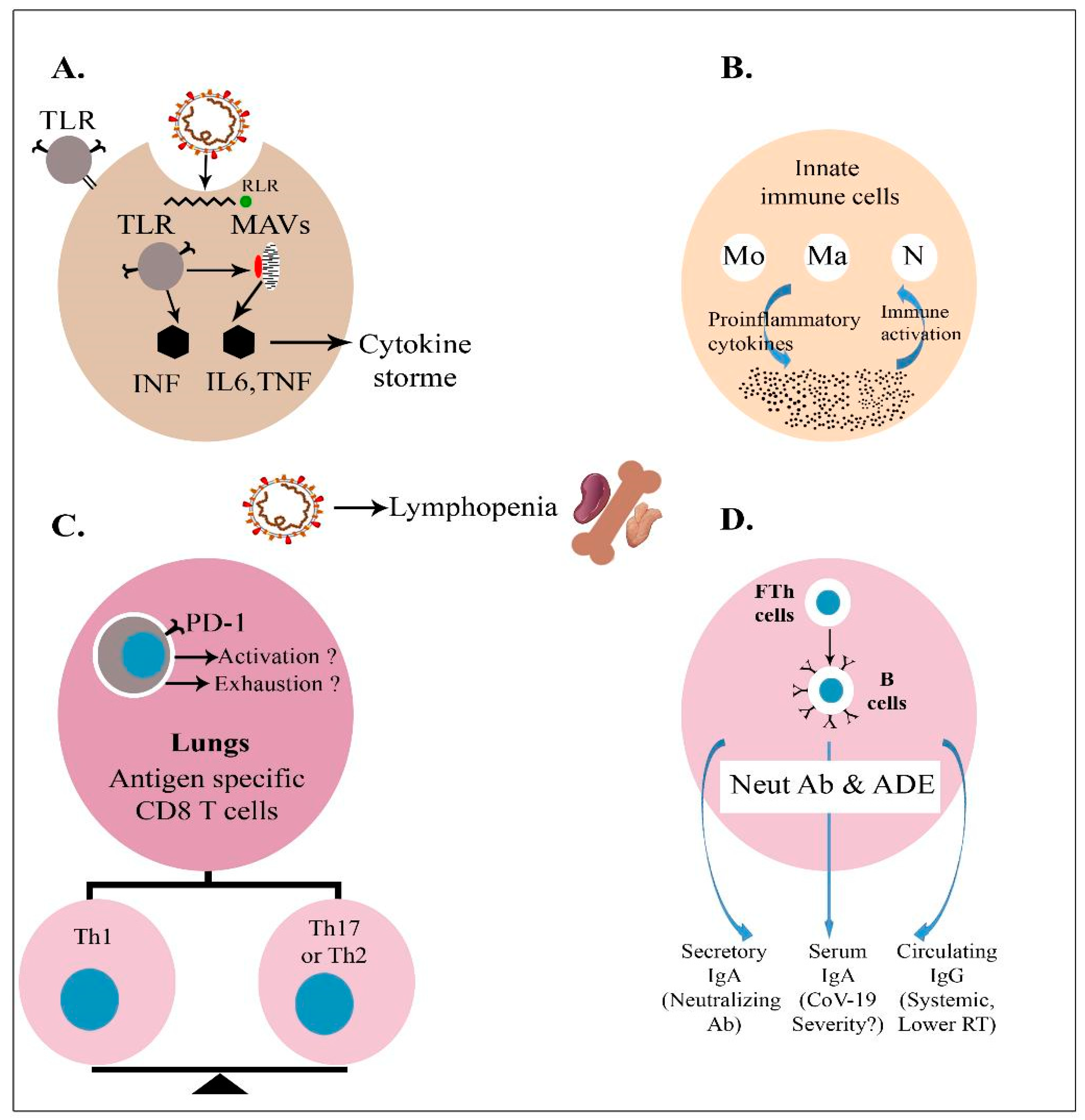
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Influenza-trained mucosal-resident alveolar macrophages confer long-term antitumor immunity in the lungs
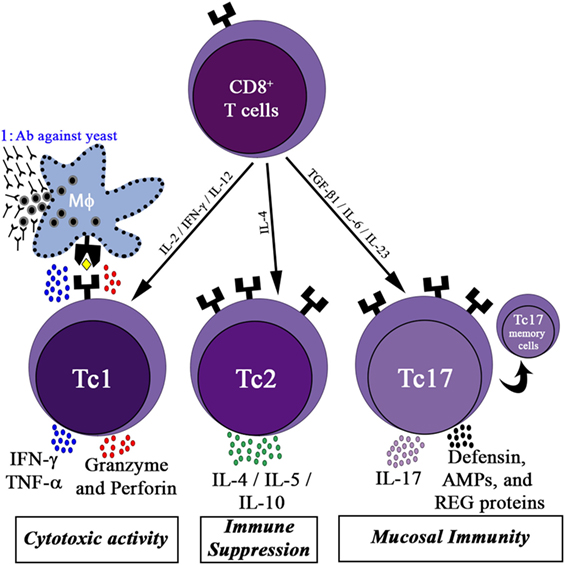
Frontiers Methods of Controlling Invasive Fungal Infections Using CD8+ T Cells
PDF] Memory CD8 T Cells: Orchestrators And Key Players Of, 50% OFF

Research outcomes
Viruses, Free Full-Text
- Flu Attack! How A Virus Invades Your Body : Krulwich Wonders : NPR

- Viral: Man shows off his body out of moving car's sunroof in UP's Ghaziabad
- Virus blocking textile for SARS-CoV-2 using human body triboelectric energy harvesting - ScienceDirect

- Can the virus enter our bodies through our skin?

- Woman goes viral for exposing how easy it is to edit your body in social media videos

- Sand Brown, Cotton Twill Fabric, 8 oz., Apparel / Slipcovers / Bedding, 54 Wide

- Member's Mark Ladies 2 Pack French Terry Luxe Full Legging - Sam's Club
- Calvin Klein Medium Double Waistband Swimshort Men

- Plus Size Quick Dry Elastic Loose Ankle-Tied High Waist Yoga Pants

- New 2014 Spring and Summer Women's Fashion Plus Size Loose Floral Printing Batwing-slee…


