The Molecular Basis of Fibrin Clot Elasticity
By A Mystery Man Writer
Molecules, Free Full-Text
Engineered Molecular Therapeutics Targeting Fibrin and the Coagulation System: a Biophysical Perspective

Elimination of fibrin γ-chain cross-linking by FXIIIa increases pulmonary embolism arising from murine inferior vena cava thrombi

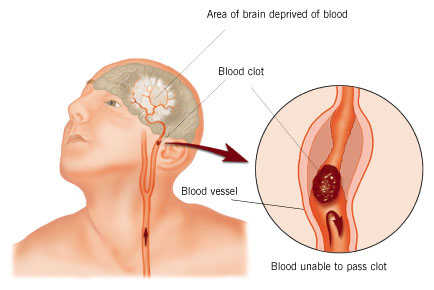
An Insight into the Abnormal Fibrin Clots — Its Pathophysiological Roles

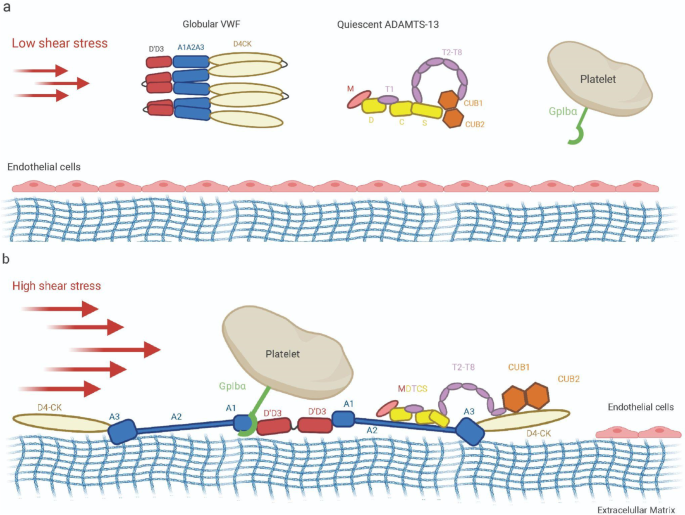
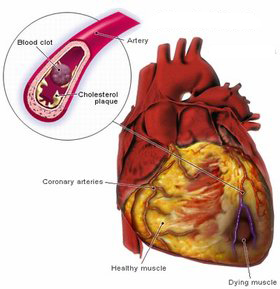
Fibrin Clot Structure and Function Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Fibrin mechanical properties and their structural origins. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Recombinant fibrinogen reveals the differential roles of α‐ and γ‐chain cross‐linking and molecular heterogeneity in fibrin clot strain‐stiffening - Piechocka - 2017 - Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis - Wiley Online Library

Flow affects the structural and mechanical properties of the fibrin network in plasma clots
The Molecular Basis of Fibrin Clot Elasticity
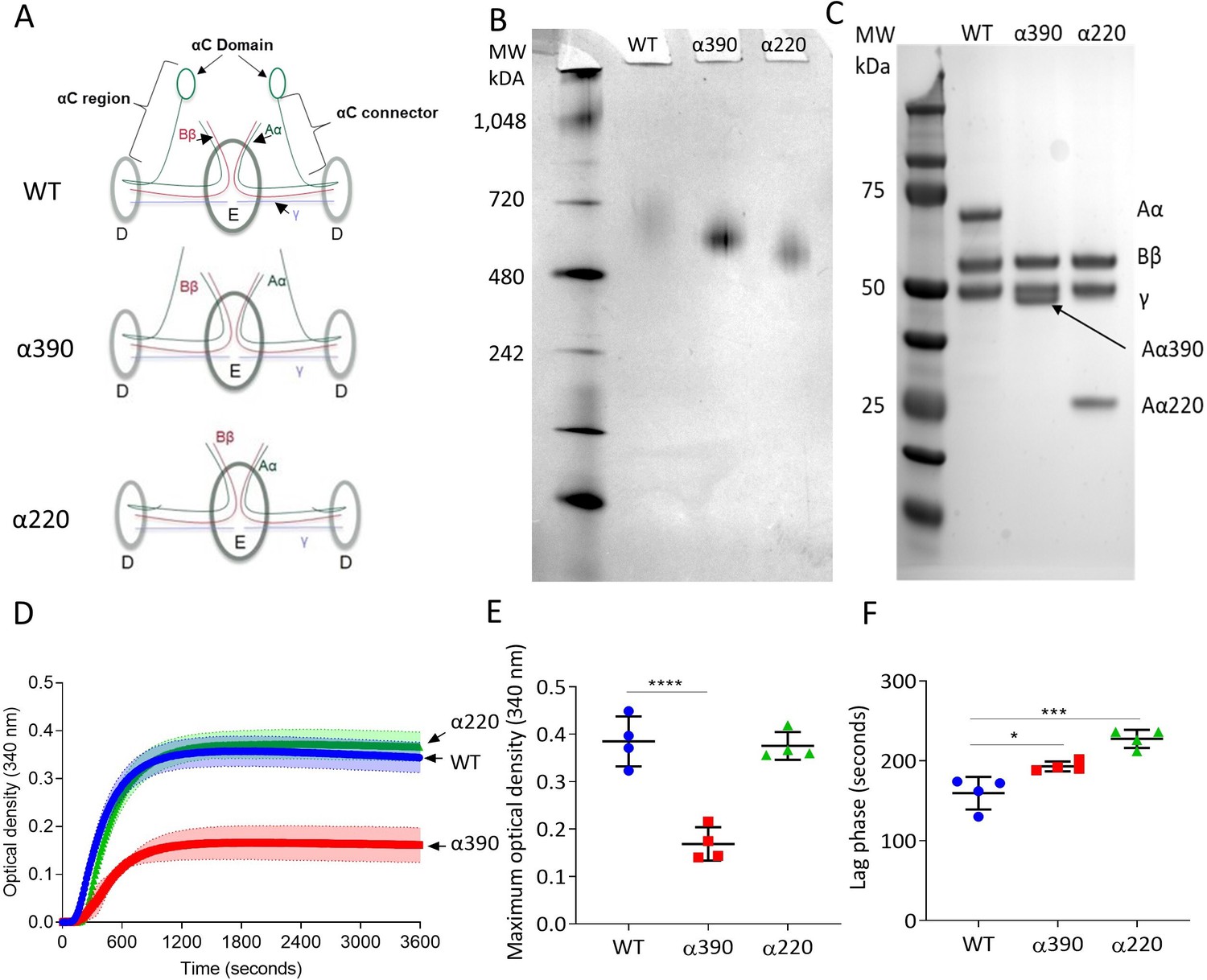
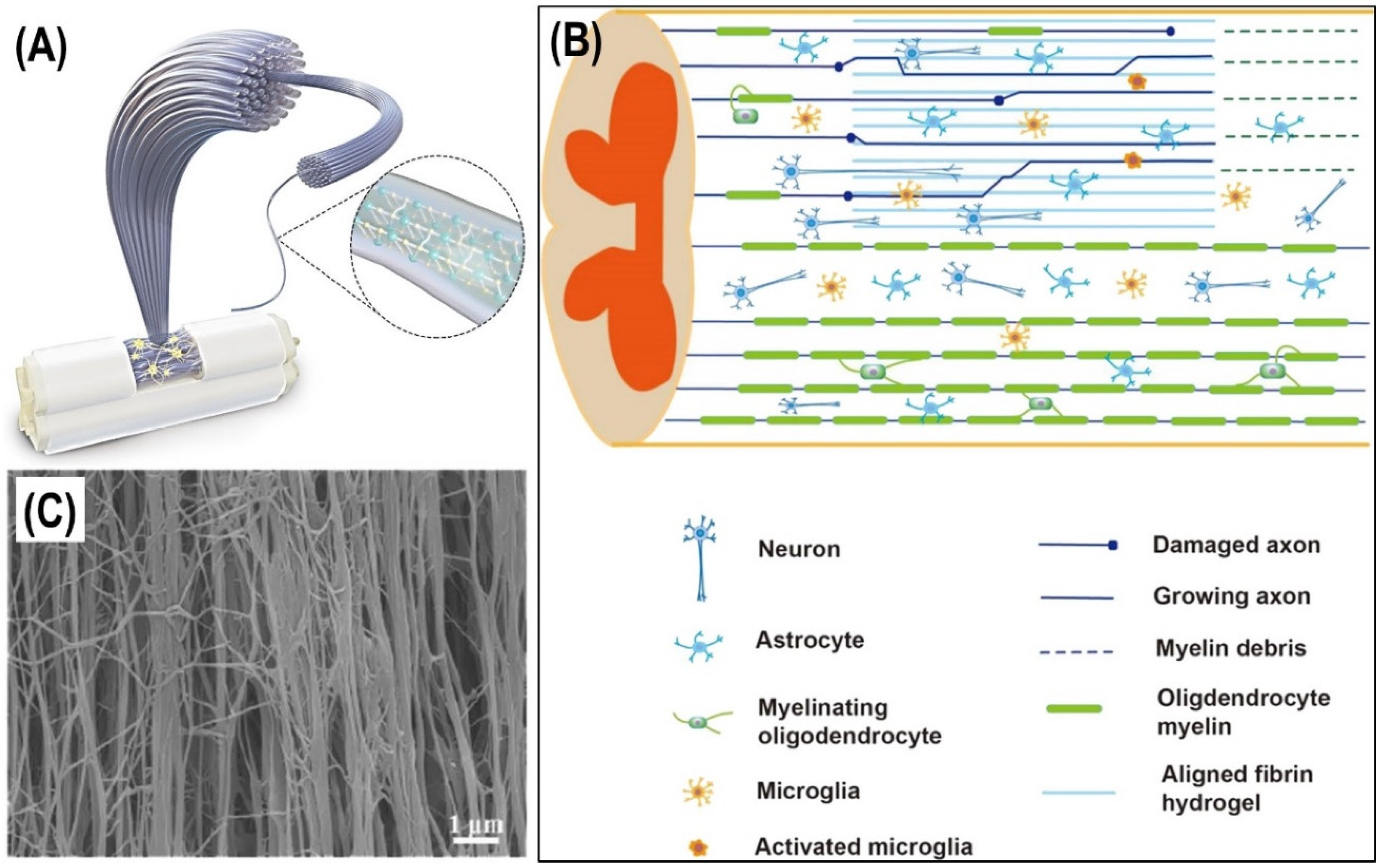
Fibrinogen αC-subregions critically contribute blood clot fibre growth, mechanical stability, and resistance to fibrinolysis
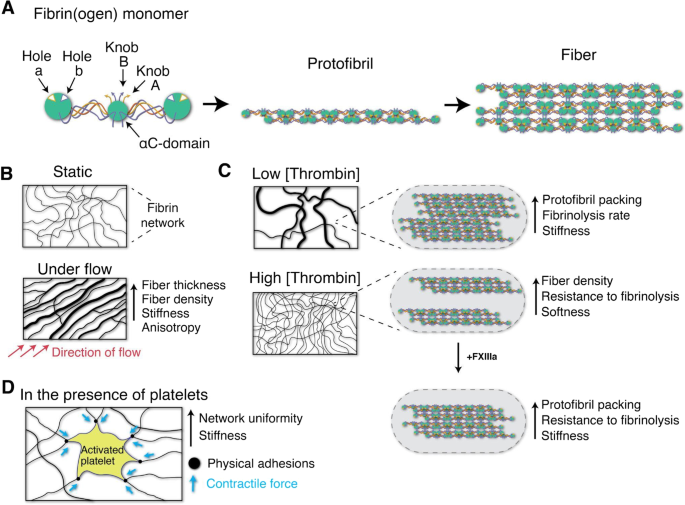
Engineered Molecular Therapeutics Targeting Fibrin and the Coagulation System: a Biophysical Perspective
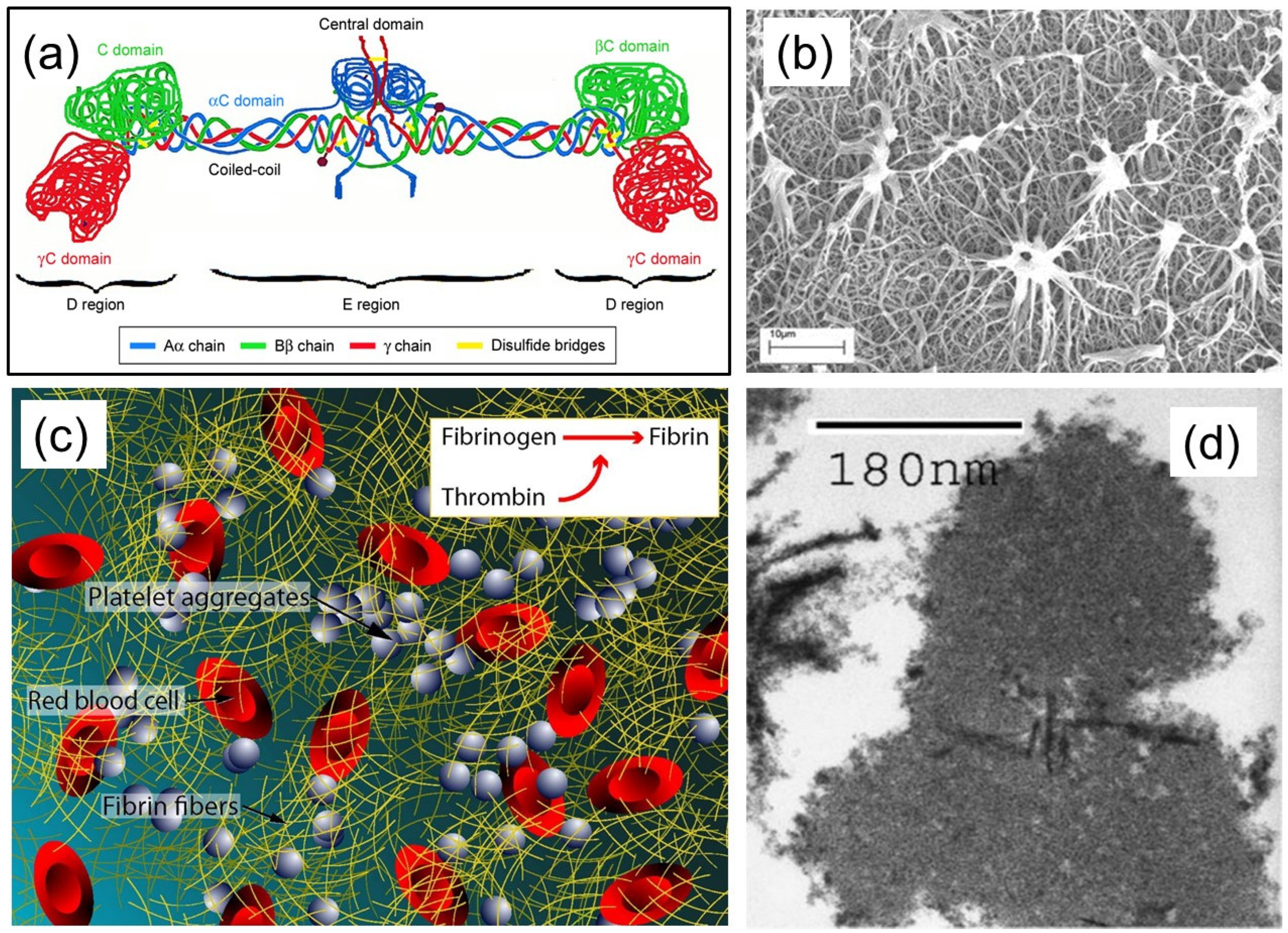
Molecules, Free Full-Text

Molecular Basis of Fibrin Clot Elasticity - ScienceDirect

Quantitative structural mechanobiology of platelet-driven blood clot contraction
- Advanced Gynecology - Passing blood clots during your period is often a normal occurrence. However, if you're changing your tampon every two hours or sooner, or are passing blood clots the size
- 14 Possible Reasons for Passing Blood Clots in Pregnancy

- Period Blood Clots: Causes & How To Manage Them

- Blood Clots After Birth: Symptoms, Treatment, and More
- Illustrations of a typical clot configuration within the flow

- Buy Wolford Mesh Shapewear Dress - Nude At 45% Off

- James O'Neill, American Experience, Official Site

- Best Minimizer Bras Large Busts, Full Coverage Bra Minimize

- CLOSED LUDWIG SATIN PANTS Woman Dark Night

- Womens Mock Neck Athletic Workout Top Long Sleeve Running Shirt(S(US Size 4-6_Bust 35-36 Inch),Black) : : Clothing, Shoes & Accessories

