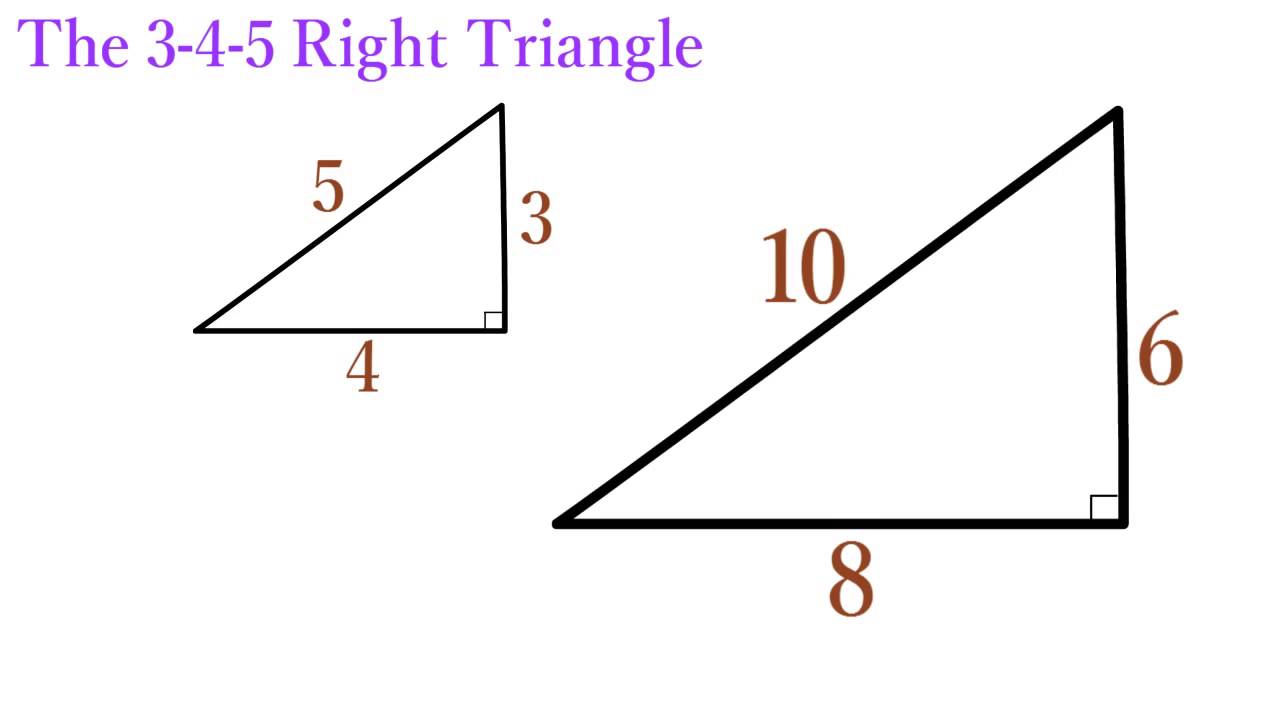
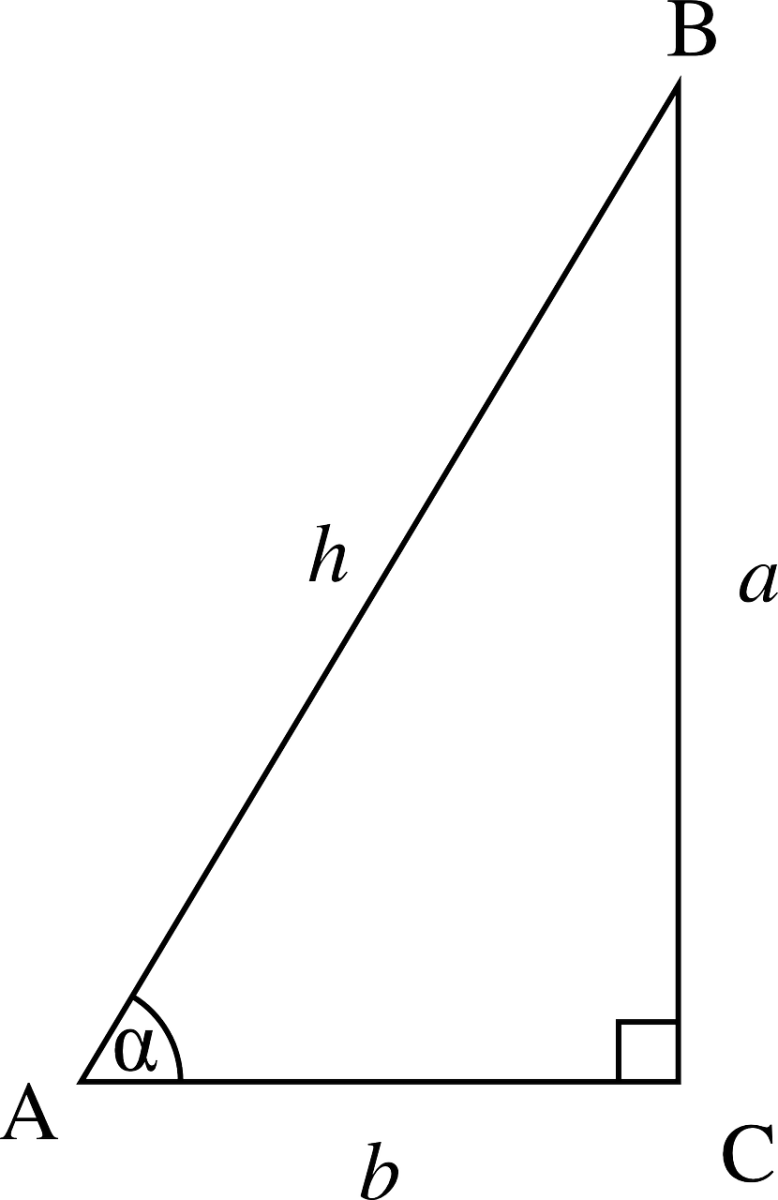
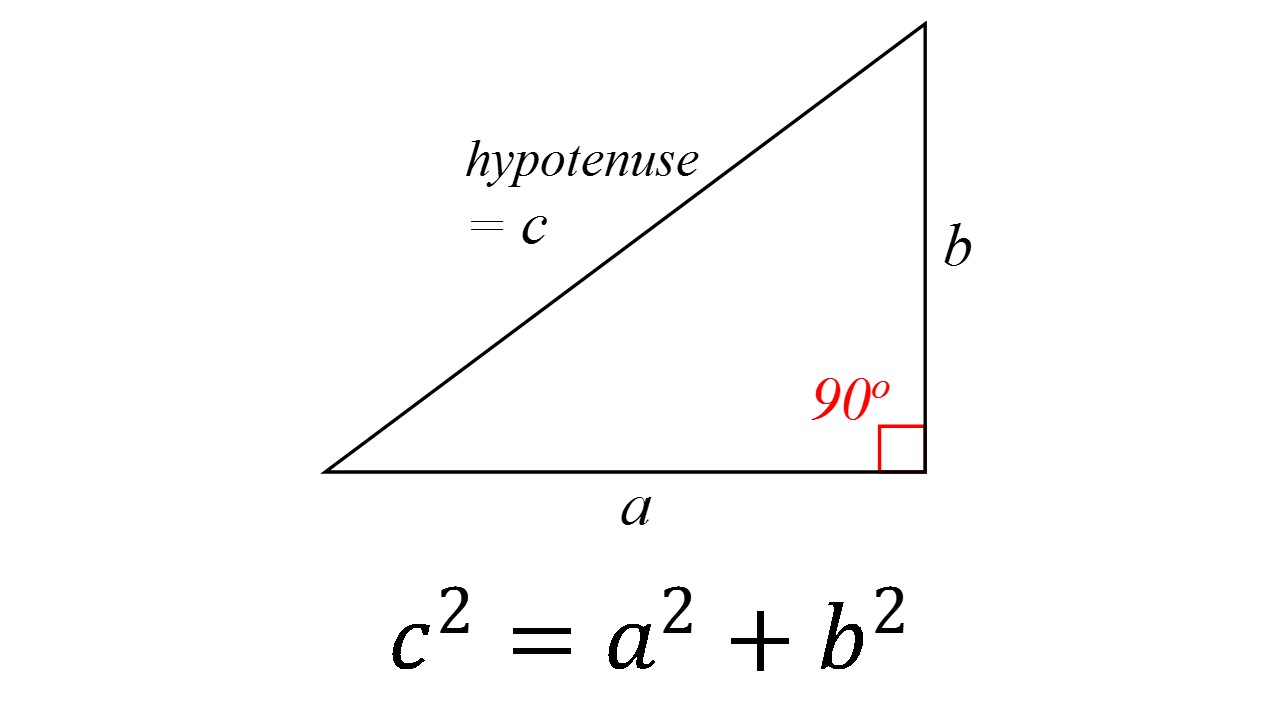
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the
By A Mystery Man Writer
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.
Can you use the Pythagorean theorem to find an angle? - Quora
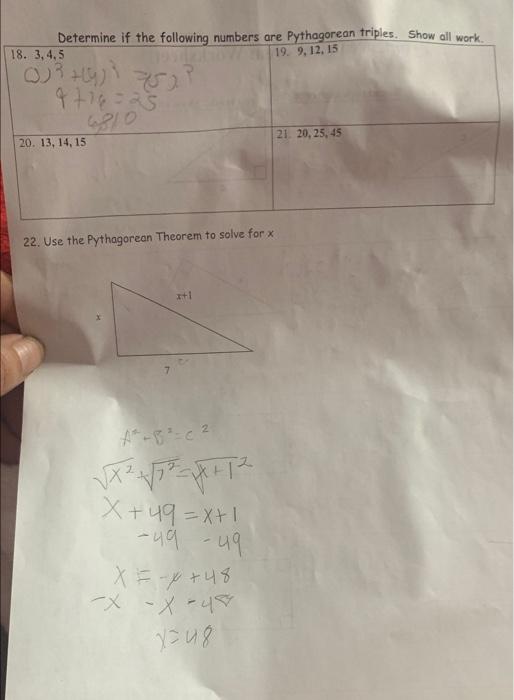
Solved 19. 9, 12, 15 Determine if the following numbers are

How to Determine Whether a Triangle is a RIGHT Triangle

Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem

IXL The Pythagorean theorem

Apply the Pythagorean theorem. Find whether the given triangle has a right angle.
Pythagoras Theorem - Formula, Proof, Examples, Applications
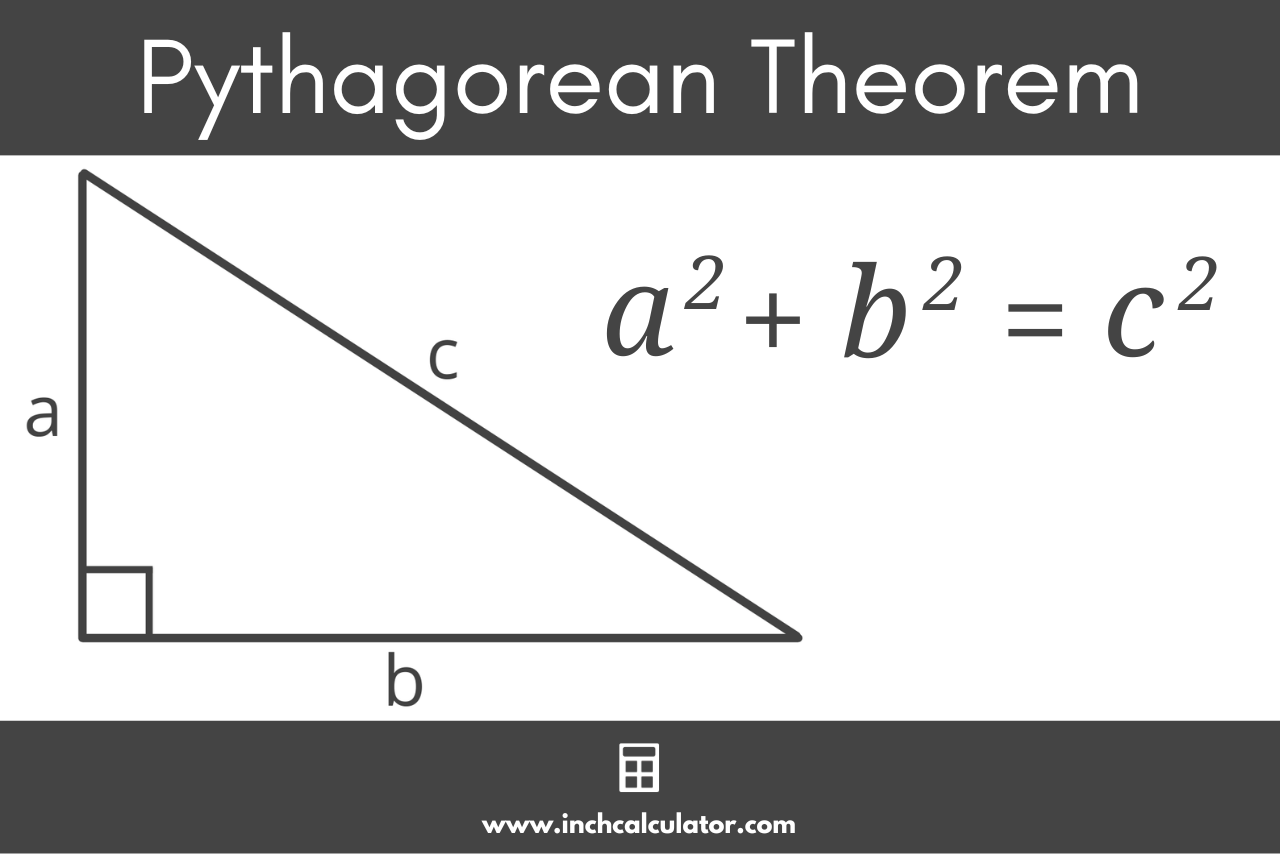
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator - Steps to Solve - Inch Calculator

URGENT. i wasn't at school all week due to the flu and I really need help on these Pythagorean theorem

Playing With Pythagoras and Trigonometry – Pondering Planning in Mathematics
- Look para el gym: Outfits que te ayudarán a encontrar tu estilo
- Mallas · adidas · Mujer · Deportes · El Corte Inglés (85)

- Yoga Pants Women's High Waist Workout Boots Pants With Pockets Belly Control, 4 Pocket Women's Work Pants

- Deep Ocean - Divine Ultrahigh-Rise Legging

- Jockey Women's Underwear Smooth & Radiant Modern Brief White Size 6