Polymers, Free Full-Text
By A Mystery Man Writer
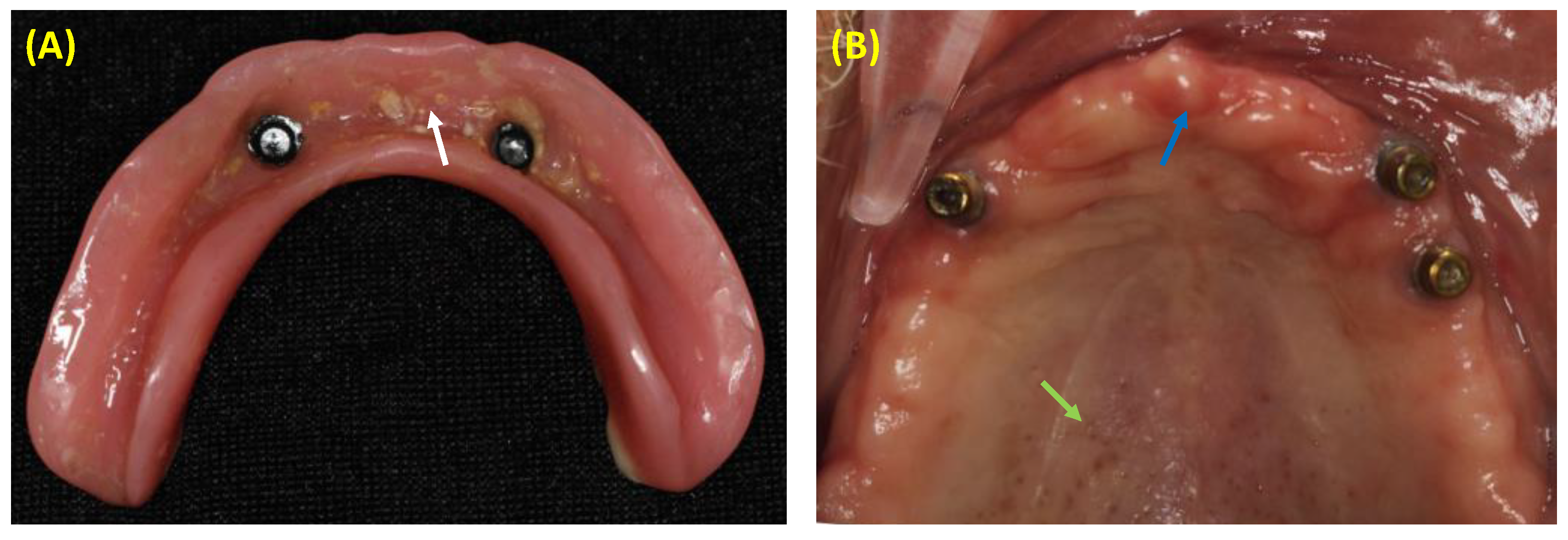
Denture base resin (DBR) materials are used in dentistry in constructing removable dentures and implant-supported prostheses. A plethora of evidence has demonstrated that DBR materials are associated with a high risk of denture stomatitis, a clinical complication where the soft oral tissues underneath the resin-based material are inflamed. The prevalence of denture stomatitis among denture wearers is high worldwide. Plaque accumulation and the infiltration of oral microbes into DBRs are among the main risk factors for denture stomatitis. The attachment of fungal species, mainly Candida albicans, to DBRs can irritate the underneath soft tissues, leading to the onset of the disease. As a result, several attempts were achieved to functionalize antimicrobial compounds and particles into DBRs to prevent microbial attachment. This review article explored the advanced approaches in designing bioactive and antimicrobial DBR materials. It was reported that using monomer mixtures, quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs), and organic and inorganic particles can suppress the growth of denture stomatitis-related pathogens. This paper also highlighted the importance of characterizing bioactive DBRs to be mechanically and physically sustainable. Future directions may implement a clinical translational model to attempt these materials inside the oral cavity.

Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
Solubility of Polymers - Materials Square
2024 Significance of area of hysteresis loop - Polymers Free Full-Text Influence of the Addition of Vital Wheat
Polymers, Free Full-Text, Conductive Thread
PPT - Polymers PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1901418

PDF) Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for - Chemosensors MDPI

High free volume polymers for pervaporation - ScienceDirect
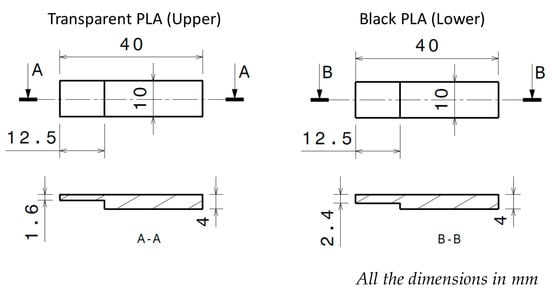
Polymers, Free Full-Text, passfeder 5mm

Polymers, Free Full-Text, passfeder 5mm
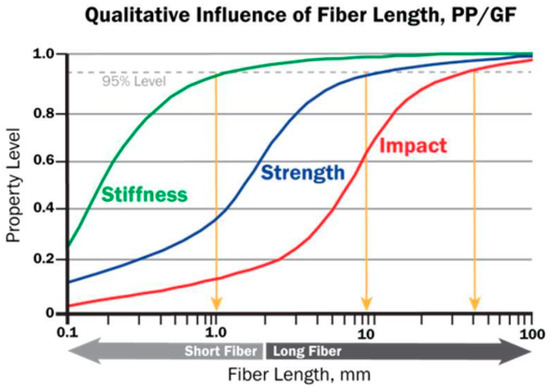
Polymers, Free Full-Text
- Esc. Mun. Profª. Ana Cristina Rolim Machado: AULA DE CAMPO NO

- Batom matte fiore fenzza make up cor 8 - Batom - Magazine Luiza

- Distribution of Burkholderia pseudomallei within a 300-cm deep soil profile: implications for environmental sampling
- Fb 03 12 2014 by Current Newspapers - Issuu

- Diário Indústria&Comércio - 06 de julho de 2017 by Diário Indústria & Comércio - Issuu





