Passive (a) and active (b) patellar tracking.
By A Mystery Man Writer
Download scientific diagram | Passive (a) and active (b) patellar tracking. from publication: EXAMINATION OF THE PATELLOFEMORAL JOINT | Patellofemoral pain is one of the leading causes of knee pain in athletes. The many causes of patellofemoral pain make diagnosis unpredictable and examination and treatment difficult. This clinical commentary discusses a detailed physical examination routine for the patient | Clinical Reasoning, Joints and Pain | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
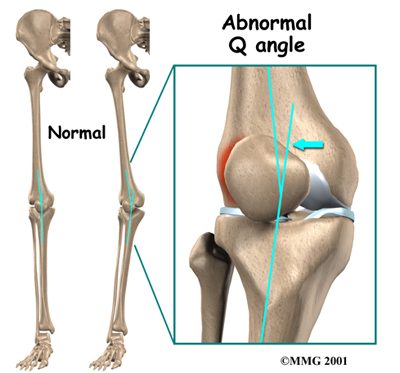
Physical Therapy in Armonk for Knee - Patellofemoral Problems

Objective assessment of patellar maltracking with 3 T dynamic magnetic resonance imaging: feasibility of a robust and reliable measuring technique
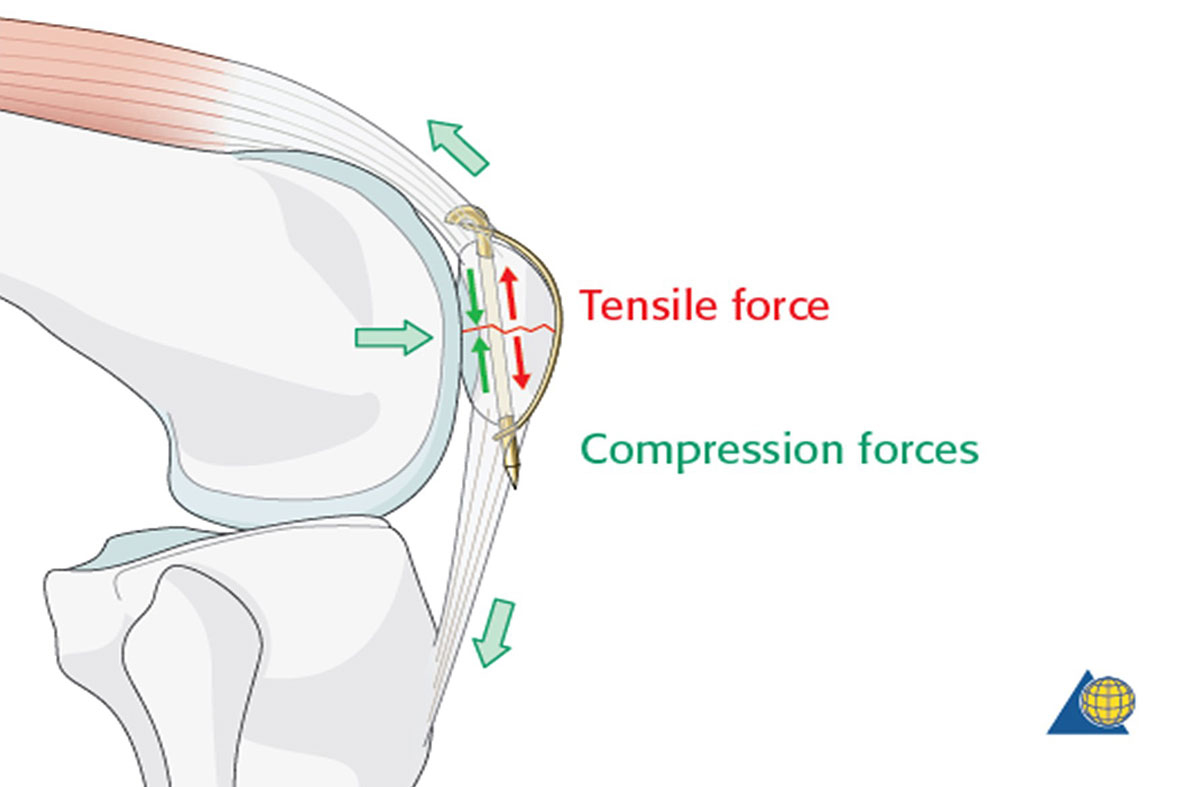
Practical guidelines for the treatment of patellar fractures in adults

PDF) EXAMINATION OF THE PATELLOFEMORAL JOINT

Ultrasound Measurement of Lateral Patellar Displacement: A Cadaveric Validation Study
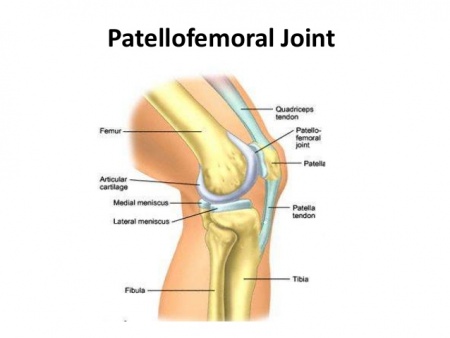
Patellofemoral Joint - Physiopedia

Common modelling assumptions affect the joint moments measured during passive joint mobilizations

Sensors, Free Full-Text

Hamstring Injuries in Athletes - Sports Medicine Review
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-184947597-1724861e629b4db595028d3639c6e163.jpg)
Range of Motion: Active, Passive, and Problems

Fixing Patellar & Quad Tendon Pain – Squat University

Patellar instability can be classified into four types based on patellar movement with knee flexion: a three-dimensional computer model analysis - ScienceDirect
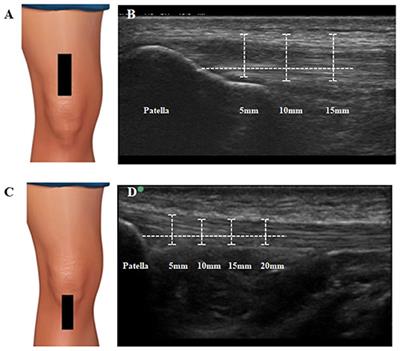
Frontiers Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Thickness and Stiffness in Elite Track Cyclists: An Ultrasonographic and Myotonometric Evaluation
- Fila WOMAN CULOTTE 3 PACK - Pants - black - Zalando.de

- Koszulka Love My Boyfriend, Kocham moją dziewczynę i jestem dumny, że to mówię T-Shirt

- Aroona Women Black Bathing Suits One Piece Swimwear with Skirt Modest Swimsuit

- PixelThat, Women's Yoga Shorts, Cute Yoga Shorts

- ASOS 4505 Pants for Women, Online Sale up to 70% off