Management of Onychomycosis and Co-Existing Tinea Pedis - JDDonline - Journal of Drugs in Dermatology

By A Mystery Man Writer
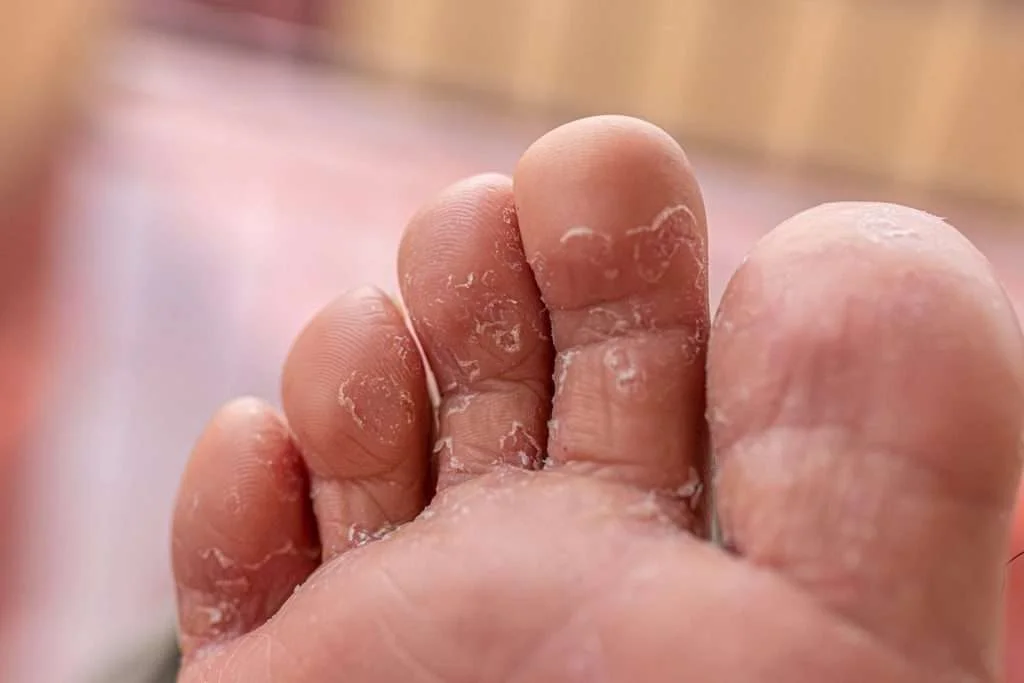
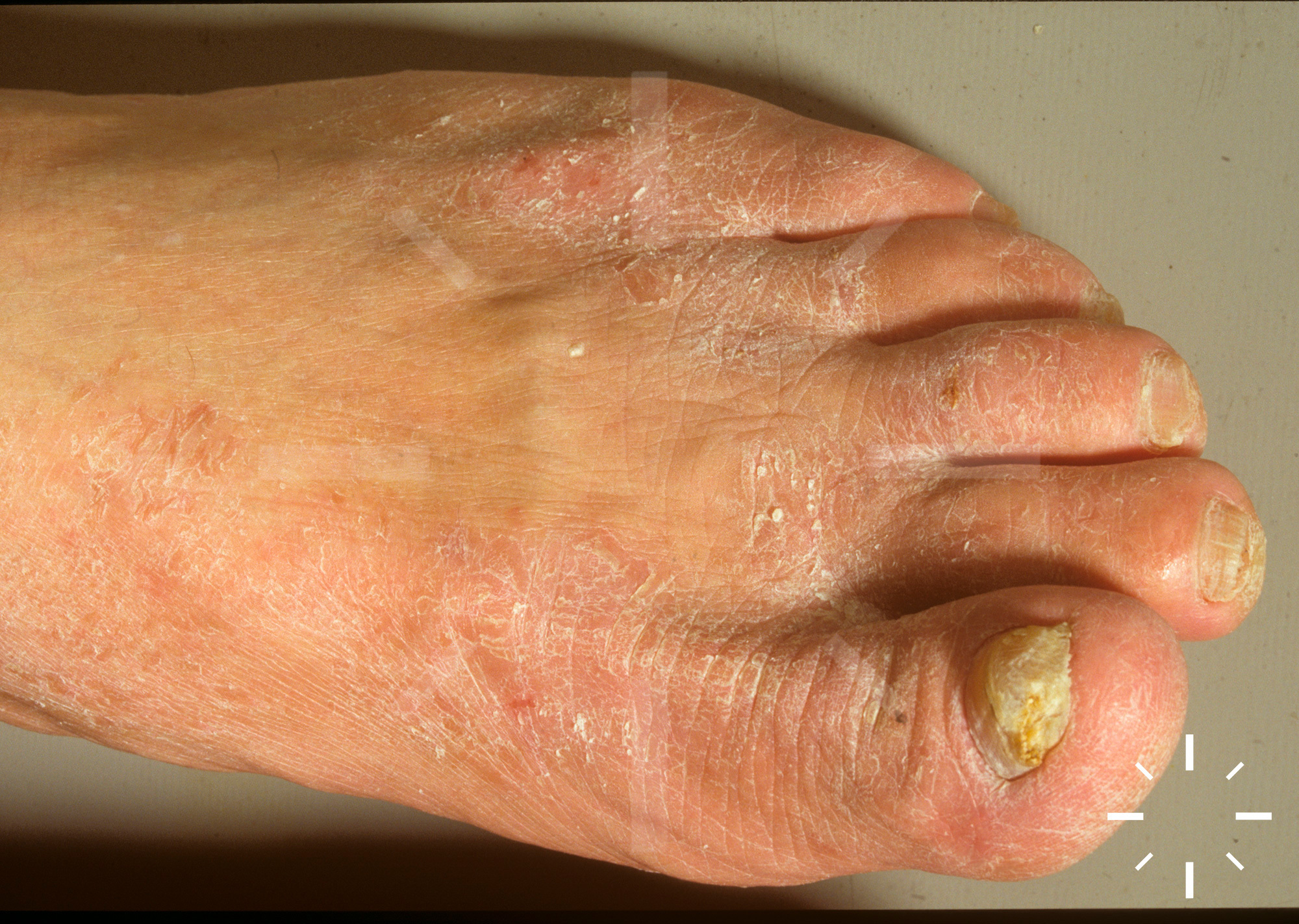
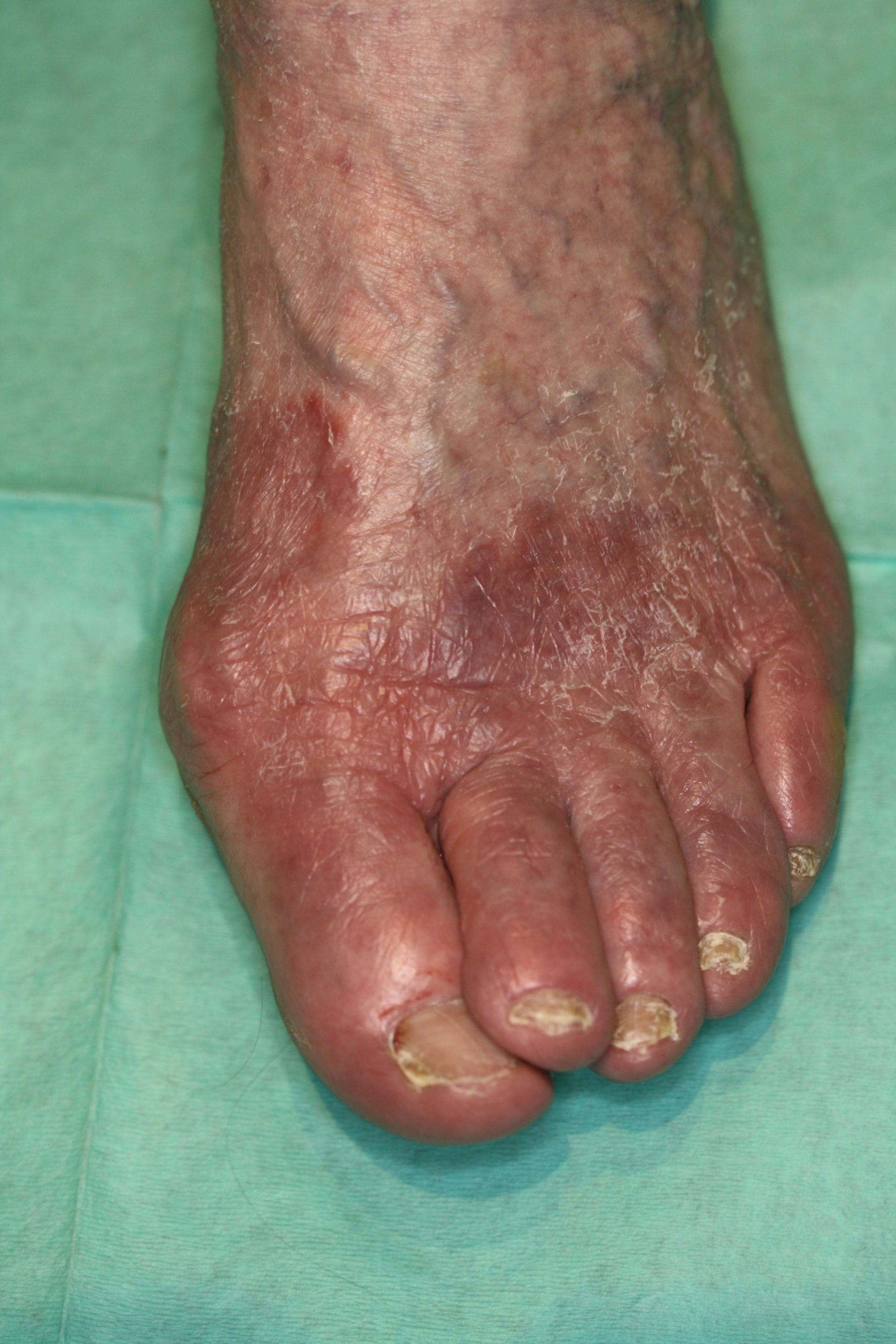
AbstractOnychomycosis is a common infection of the nail that often co-exists with tinea pedis. Surveys have suggested the diseases co-exist in at least one third of patients, although actual numbers may be a lot higher due to significant under-reporting. The importance of evaluating and treating both diseases is being increasingly recognized, however, data on improved outcomes, and the potential to minimize re-infection are limited. We review a recent post hoc analysis of two large studies treating mild to moderate onychomycosis with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, demonstrating that complete cure rates of onychomycosis are significantly improved when any co-existing tinea pedis is also treated.J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14(5):492-494. Onychomycosis, Proximal Subungual, Distal Subungual, Tinea Unguium, Tinea PedisOnychomycosis, Proximal Subungual, Distal Subungual, Tinea Unguium, Tinea Pedis

Update: medical treatment of onychomycosis - Shemer - 2012

PDF) Detection and relevance of naftifine hydrochloride in the

New Topical Therapeutic Options in the Management of Superficial

Onychomycosis: Novel strategies for treatment - ScienceDirect
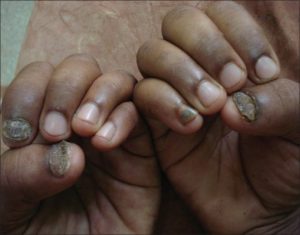
Fungus Among Us: Practical Case-Based Pearls for the Diagnosis and

Onychomycosis in Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnosis, and
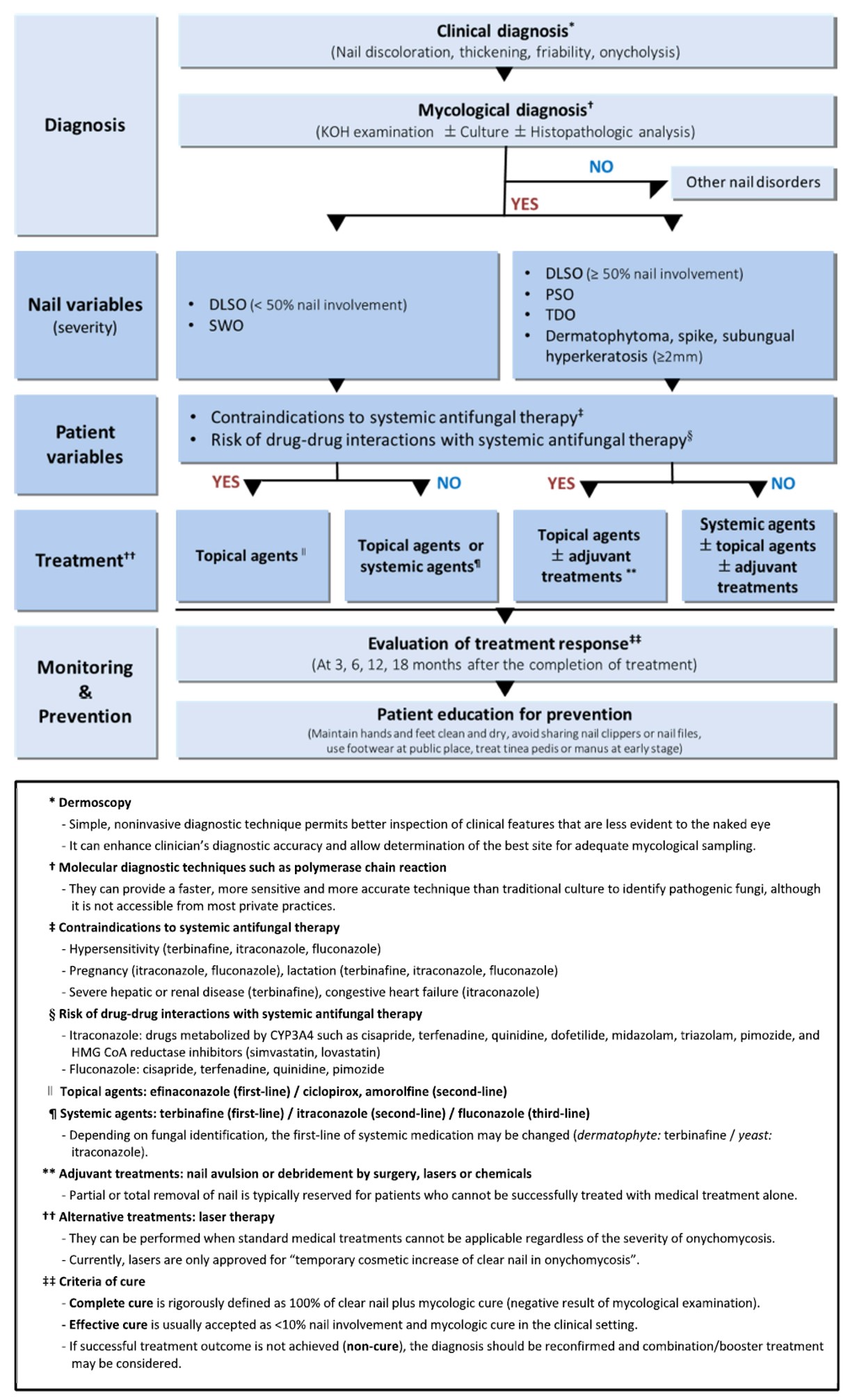
JMI - The Journal of mycology and infection
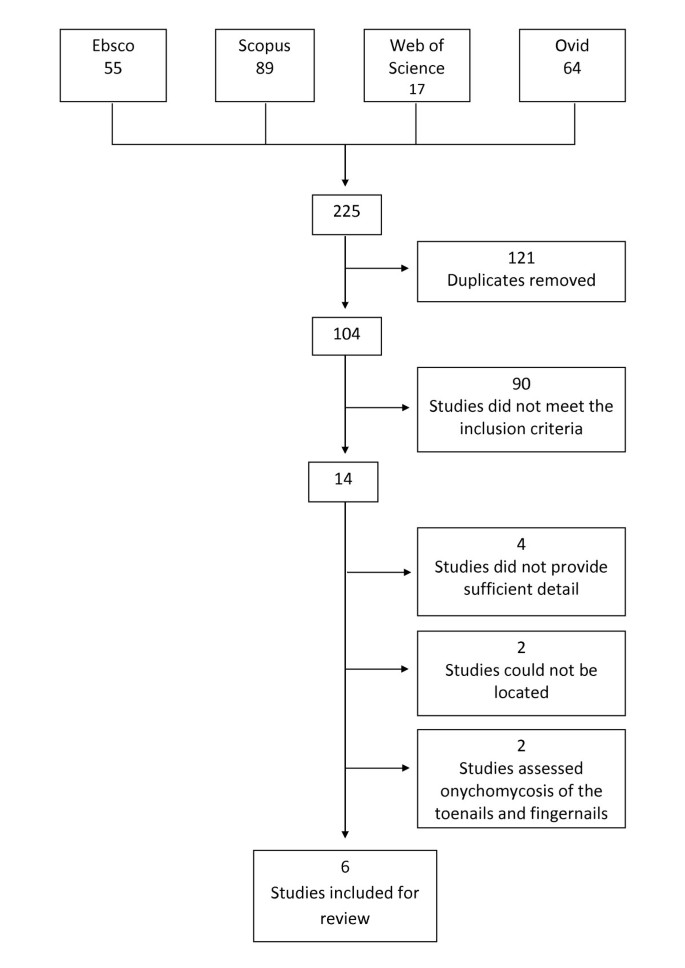
Safety and efficacy of tinea pedis and onychomycosis treatment in

PDF) Detection and Relevance of Naftifine Hydrochloride in the
- Petite Black Jeggings

- Vision Of Super flame-print logo-print Bodysuit - Farfetch

- Kids Girls Cotton Crop Top Ribbed Bra Vest Spaghetti Straps Solid Color Basic Camisole Underwear Casual Gym Fitness Sportwear - AliExpress

- Disposable Diaper Size 1 (8-14lbs) - Young At Heart

- Women's Organic Cotton Vintage Rib Lace Trim Cami Top in Eclipse Navy