Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches

By A Mystery Man Writer
Download scientific diagram | Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches in each season. Error bars are one standard error. Data from fall were excluded due to dry conditions at the upper reach. An asterisk next to the season designates a significant difference (α = 0.05) between reaches within that season. from publication: Influence of a Spring on Fish Communities and Habitat in an Ozark Stream | Springs influence water temperature and flow of streams; however, little information exists on the effects of springs on fish communities and their potential as refugia. This study examined the impacts of a spring on a wadeable stream. Fish, water quality, and physical | Fishing Communities, Streams and Upstream | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Escape Velocity of Earth: Definition, Formula, Derivation & FAQs
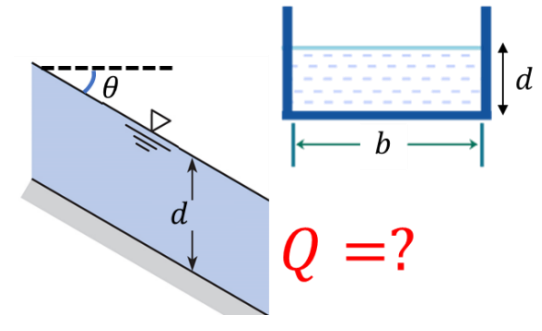
Solved water flows in a smooth open channel with a

Species richness (a) and number of intolerant species (b) for lower and

Number of respondents for each scenario

Currents, Waves, and Tides

Relationships of water velocity, stream depth and width, and friction

Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches

Flow Rate and Its Relation to Velocity

Mean water temperature (a), dissolved oxygen (b), and pH (c) at lower
Subduction - Wikipedia
- a, b. Jet width definition Download Scientific Diagram

- Mean dynamic current versus a) Transistor Width and b) Gate Length

- Brady 80067 30 Width X 30 Height B-995 Diamond Grade Reflective on Aluminum, Black on Reflective Yellow and Green Standard Traffic Sign, Pedestrians Pictogram : : Industrial & Scientific

- Beam (nautical) - Wikipedia
- Red Tartan Letter B - Scottish Patter - Bawhair Definition





