Dangers of Propane Gas - Common Causes and What to Do After a Gas
By A Mystery Man Writer
Authored by Kalamazoo injury lawyer, Steve Weston The term “natural gas” actually encompasses several types of gases, including propane, butane, ethanol, and methane. Propane is separated from these other gases and sold for residential and commercial uses. It is naturally odorless and colorless and requires the addition of an odorant so humans can detect it in case of a gas leak. Propane is pressurized into a liquid state for storage and transportation and is therefore called “liquified propane” or LP. Because of this pressurization, even a small discharge of liquified propane will create a serious hazard of ignition or explosion.

10 Common Propane Tank Problems (and how to take care of them)

WednesdayWisdom: What Causes Black Soot From A Propane Burner?

Dangers of Propane Gas - Common Causes and What to Do After a Gas Explosion and Fire - Sinas Dramis Law Firm

Benefits and Drawbacks of Propane as Generator Fuel Source

What Are the Signs of a Propane Gas Leak?

Liquid petroleum gas (LPG) safety - WorkSafe ACT

Propane Forklift Fuel System Troubleshooting: A Step-By-Step Guide

Common Gas Fireplace Problems and Fireplace Repair [With Pictures]

Cylinder and Equipment Safety - Compressed Gas Association

Michigan Burn Injury Lawyer Attorneys for Burn Injury Survivors
Chemical hazard sign for extremely combustible substances.

Chemical GHS Signs - Propane

Different Types of Gas Bottles Used in the Workplace

The Real Dangers of a Gas Leak - Refined Plumbing Sunshine Coast
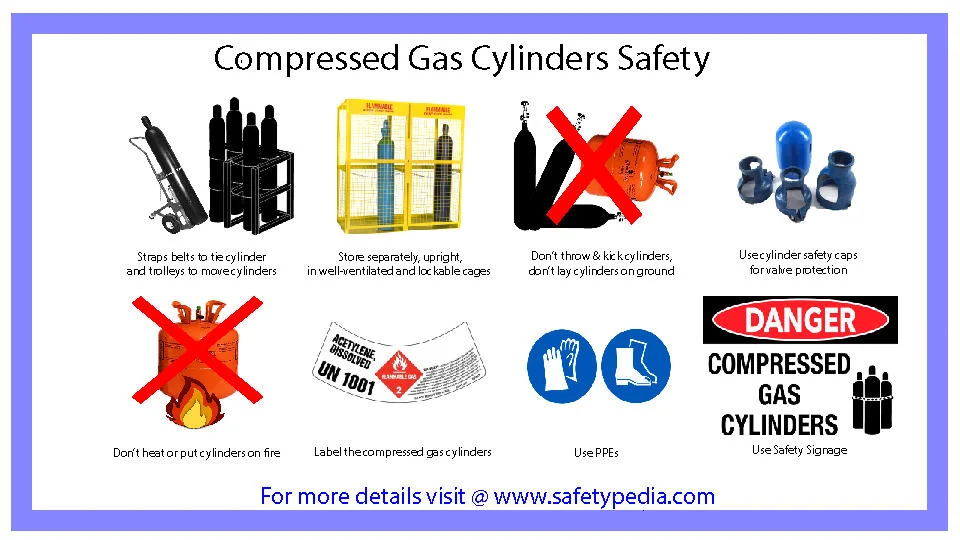
Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety and Storage - SafetyPedia

5 Differences Between Natural Gas and Propane
- Where to recycle camping fuel tanks: hint - it's not your blue box

- Are Liquid Propane Leaks Really 270 Times Larger Than Gas? Case Study Regarding The Physics Of Liquid And Gas Propane Leaks

- BernzOmatic All-Purpose Propane Fuel Cylinders, 2-Pack at Tractor Supply Co.
- What Are the Signs of a Propane Gas Leak?

- C-M Propane Fuel, 16 oz, Propane Camping Cylinde 4-Pack : Sports & Outdoors

- Oalka Women's Padded sports Bra Tank Top with Strappy Back in Size

- Mixed Lot of Barbie Accessories, camera, brushes, hair clips

- Ladies Undergarments
- Women's Nike Sportswear Club Fleece Mid-Rise Oversized Cargo Sweatpants
- Lady Gaga Once Wore This Cult-Loved Bra as a Whole Outfit — and It's Over $20 Off Today


)
