Characteristics and mechanisms of resorption in lumbar disc
By A Mystery Man Writer
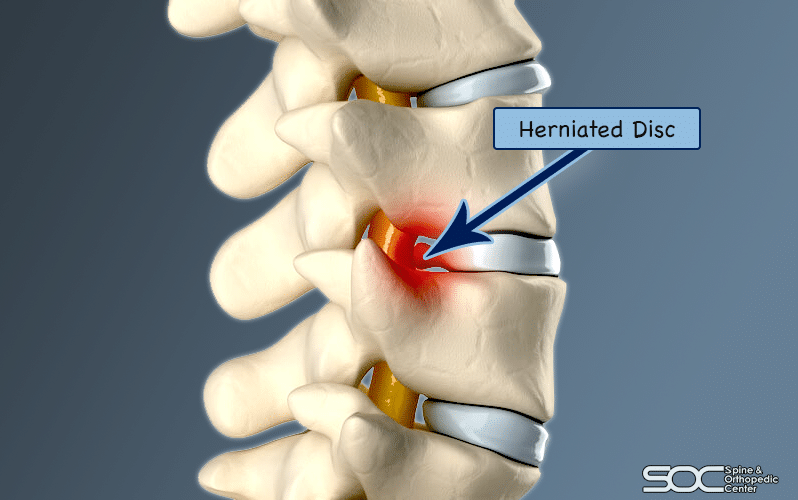
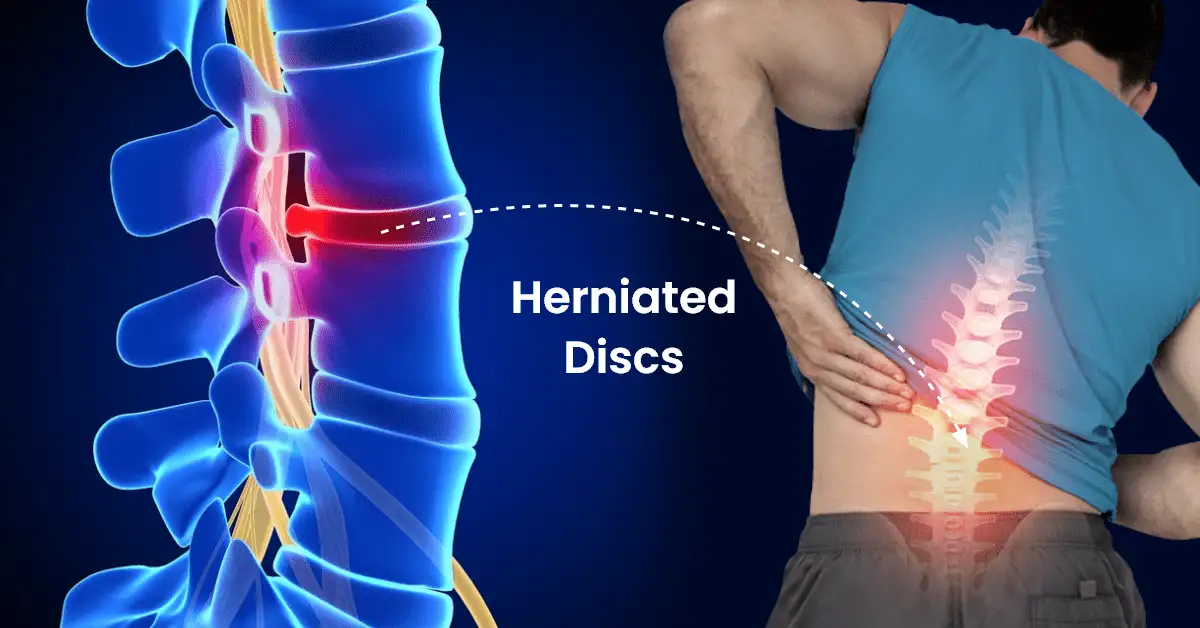
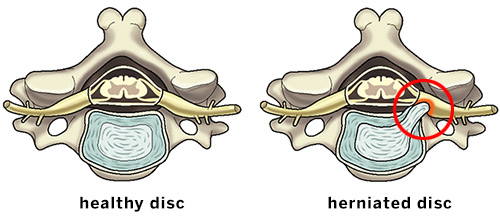
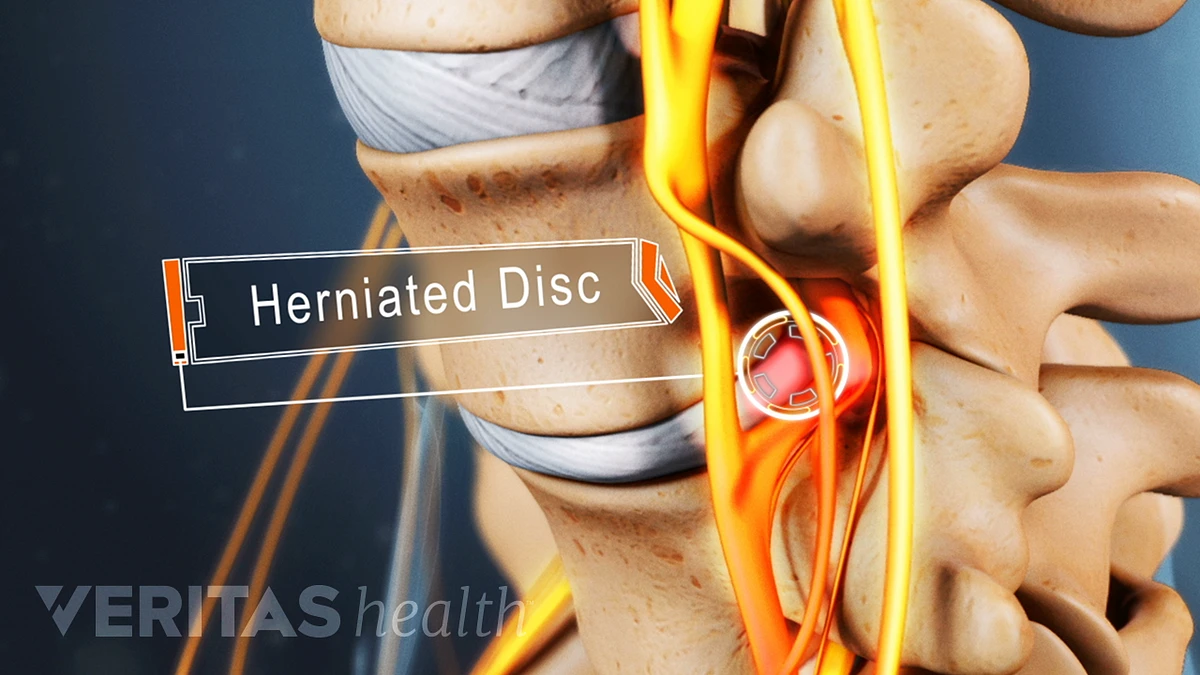
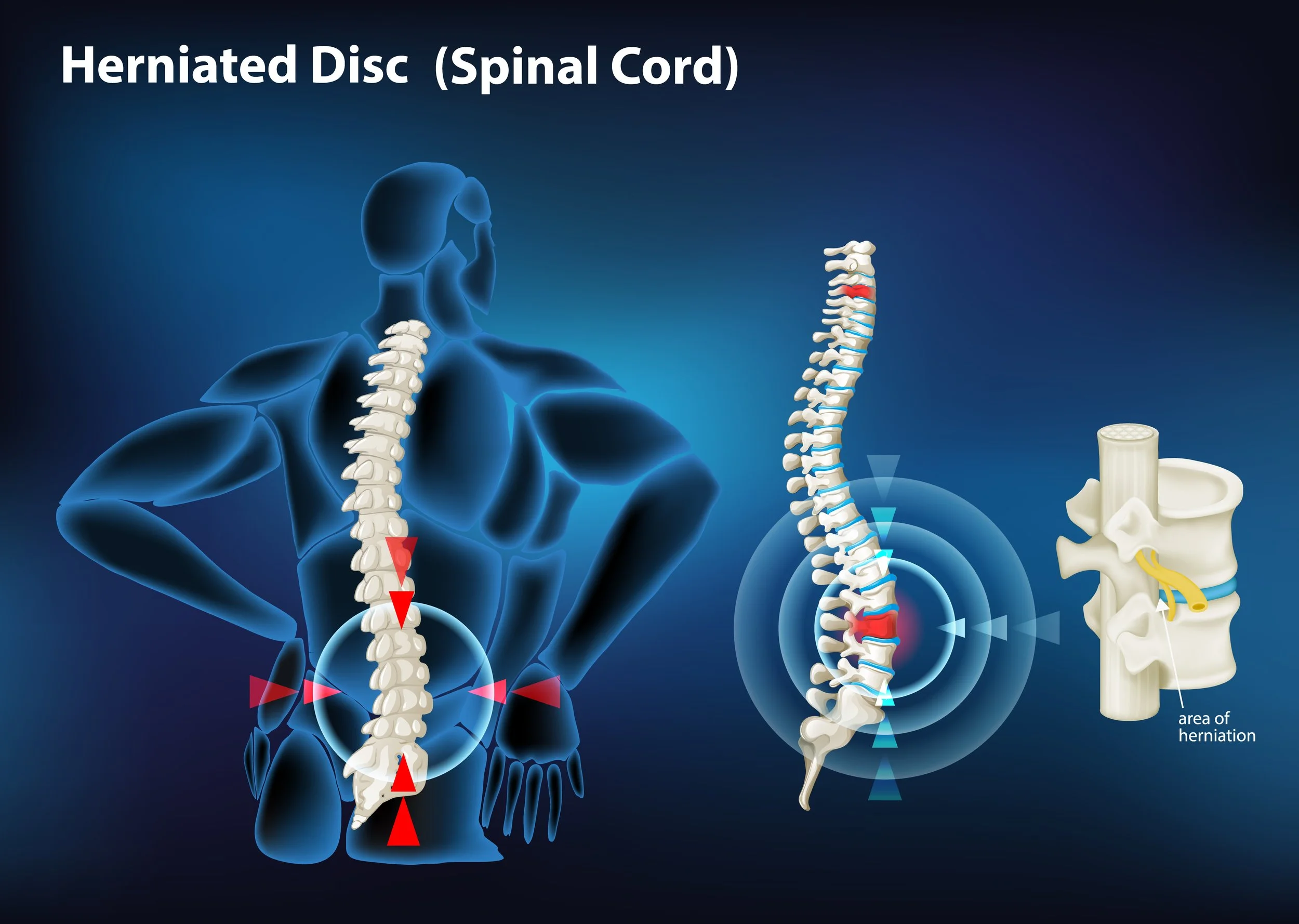
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) can be spontaneously absorbed without surgical treatment. However, the pathogenesis and physiological indications for predicting protrusion reabsorption are still unclear, which prevents clinicians from preferentially choosing conservative treatment options for LDH patients with reabsorption effects. The purpose of this review was to summarize previous reports on LDH reabsorption and to discuss the clinical and imaging features that favor natural absorption. We highlighted the biological mechanisms involved in the phenomenon of LDH reabsorption, including macrophage infiltration, inflammatory responses, matrix remodeling, and neovascularization. In addition, we summarized and discussed potential clinical treatments for promoting reabsorption. Current evidence suggests that macrophage regulation of inflammatory mediators, matrix metalloproteinases, and specific cytokines in intervertebral disc is essential for the spontaneous reabsorption of LDH.

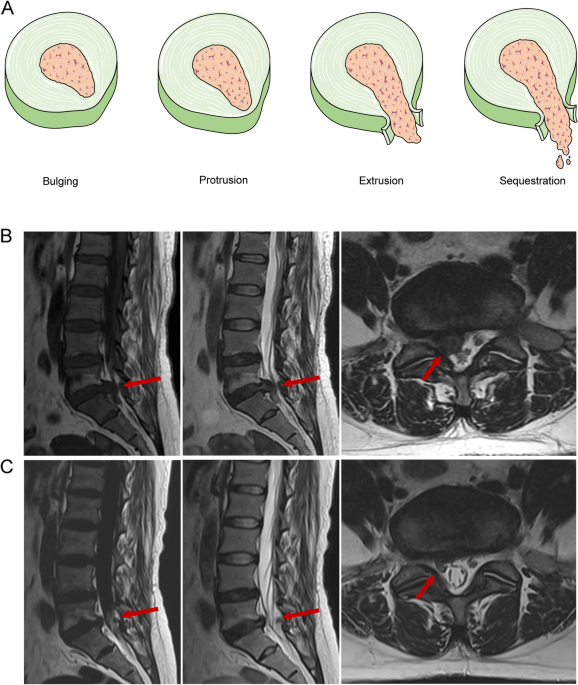
A stratified comparison (based on lumbar spine location) of disc
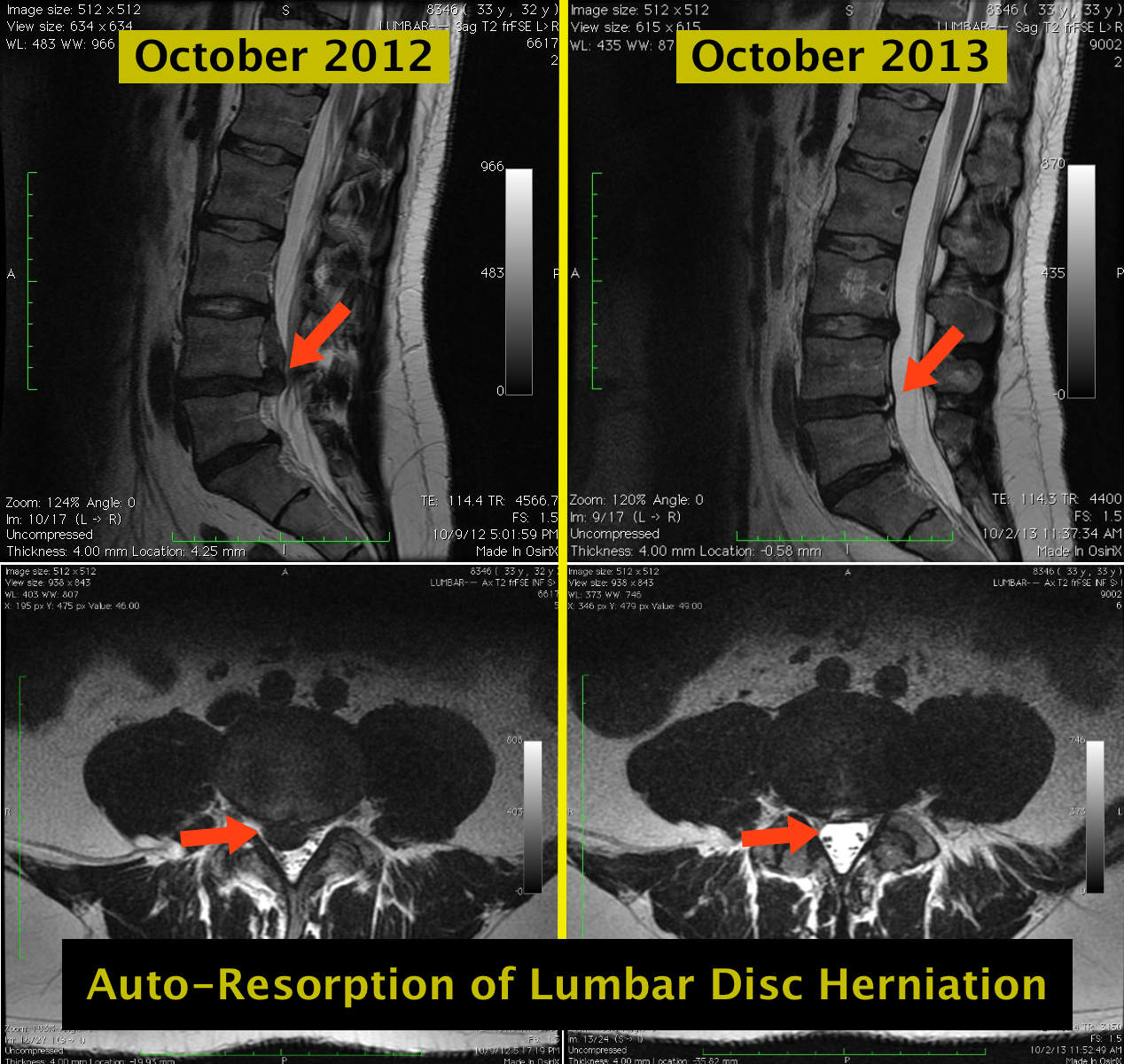
Auto-Resorption of Lumbar Disc Herniation - The Pain Source

ABCs of the degenerative spine, Insights into Imaging

Current Knowledge and Future Therapeutic Prospects in Symptomatic

Analysis of the therapeutic effect and postoperative complications associated with 3-dimensional computed tomography navigation-assisted intervertebral foraminoscopic surgery in lumbar disc herniation in the elderly: a retrospective cohort study - Yang

PDF] The predictive factors for the resorption of a lumbar disc

Neurospine

Advances in bone regeneration with growth factors for spinal

Model of MMP, macrophage, and chondrocyte interactions in HD

Spontaneous Resorption of Herniated Lumbar Disk: Observational