Blue carbon - resource

By A Mystery Man Writer
Blue carbon is the carbon stored in coastal and marine ecosystems. Coastal ecosystems such as mangroves, tidal marshes and seagrass meadows sequester and store more carbon per unit area than terrestrial forests and are now being recognised for their role in mitigating climate change. These ecosystems also provide essential benefits for climate change adaptation, including coastal protection and food security for many coastal communities. However, if the ecosystems are degraded or damaged, their carbon sink capacity is lost or adversely affected, and the carbon stored is released, resulting in emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) that contribute to climate change. Dedicated conservation efforts can ensure that coastal ecosystems continue to play their role as long-term carbon sinks.

What are blue carbon projects?

Sustainably developing global blue carbon for climate change mitigation and economic benefits through international cooperation

Coastal blue carbon in China as a nature-based solution toward carbon neutrality - ScienceDirect

Blue carbon - resource

Global trends and prospects of blue carbon sinks: a bibliometric analysis

Oceans, Free Full-Text
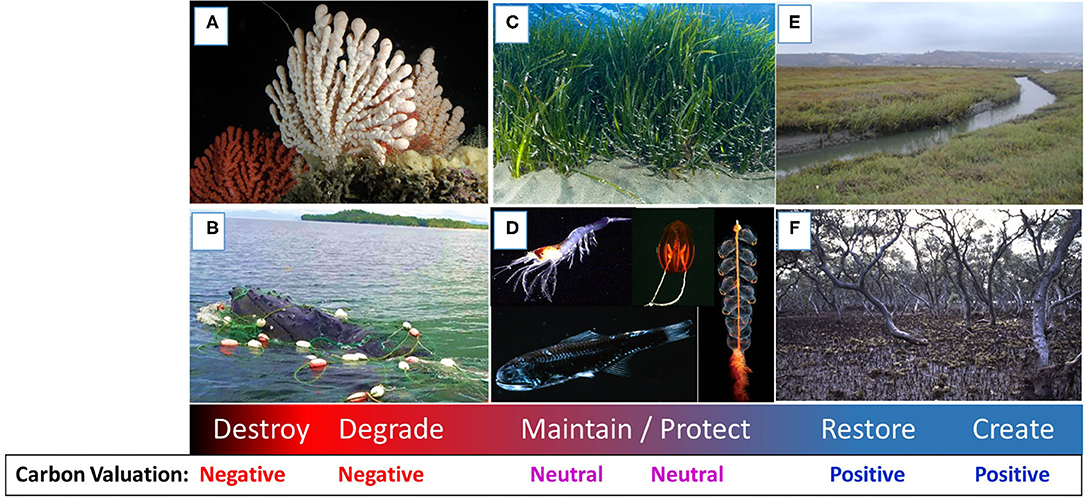
Frontiers The Role of Blue Carbon in Climate Change Mitigation and Carbon Stock Conservation

Light For Nature (LINAT) on LinkedIn: #environment #conservation #mangroves
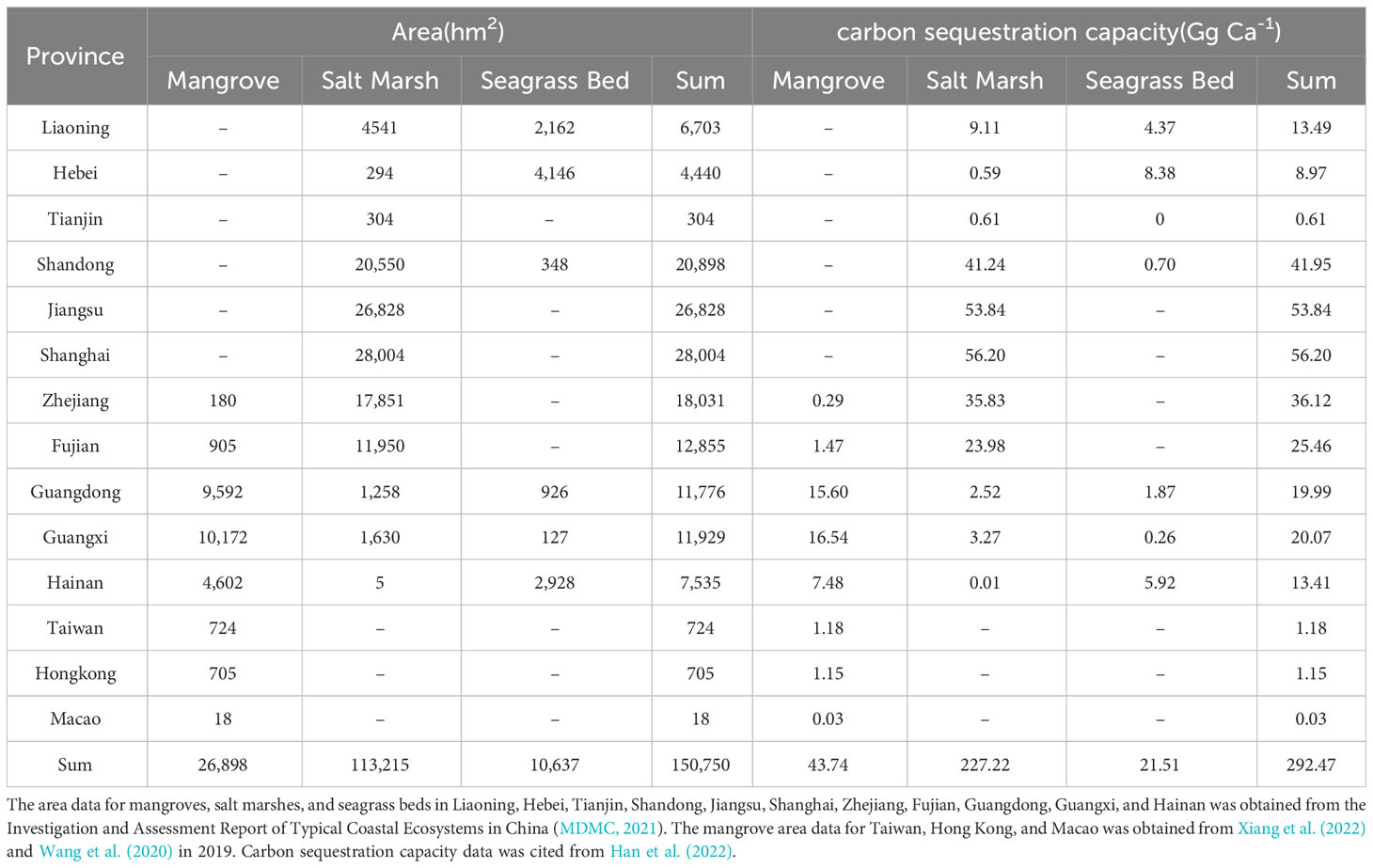
Frontiers Blue carbon development in China: realistic foundation, internal demands, and the construction of blue carbon market trading mode

The Future of Blue Carbon Conservation: Introducing the Blue Carbon Collaborative - WILDCOAST

The connected macroalgal-sediment system at Station L4. (a) Seasonal

The Environmental and Economic Potential of Kelp as Blue Carbon: Case of Hakodate, Japan
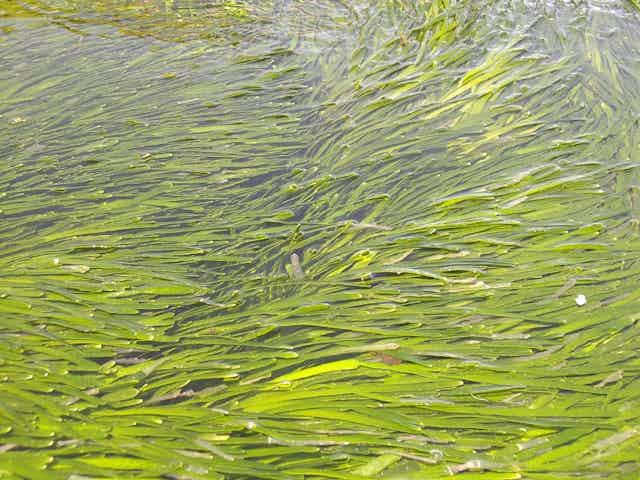

Seagrass is a huge carbon store, but will government value it?
- Maidenform Flexees Brief All Over Smoothing Black Cool Comfort Size 2xl for sale online

- Olga, Intimates & Sleepwear, Olga By Warners Beige Bra Size 42d

- Brass Wool Coarse Grade - 1lb Roll - by Rogue River Tools. Made in USA, Pure Brass

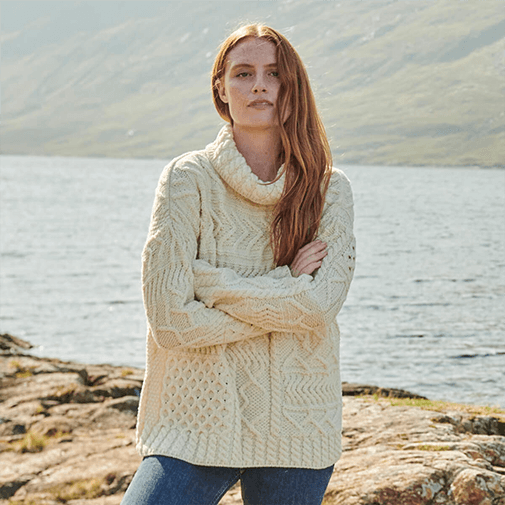
- Patchwork Oversized Aran Sweater

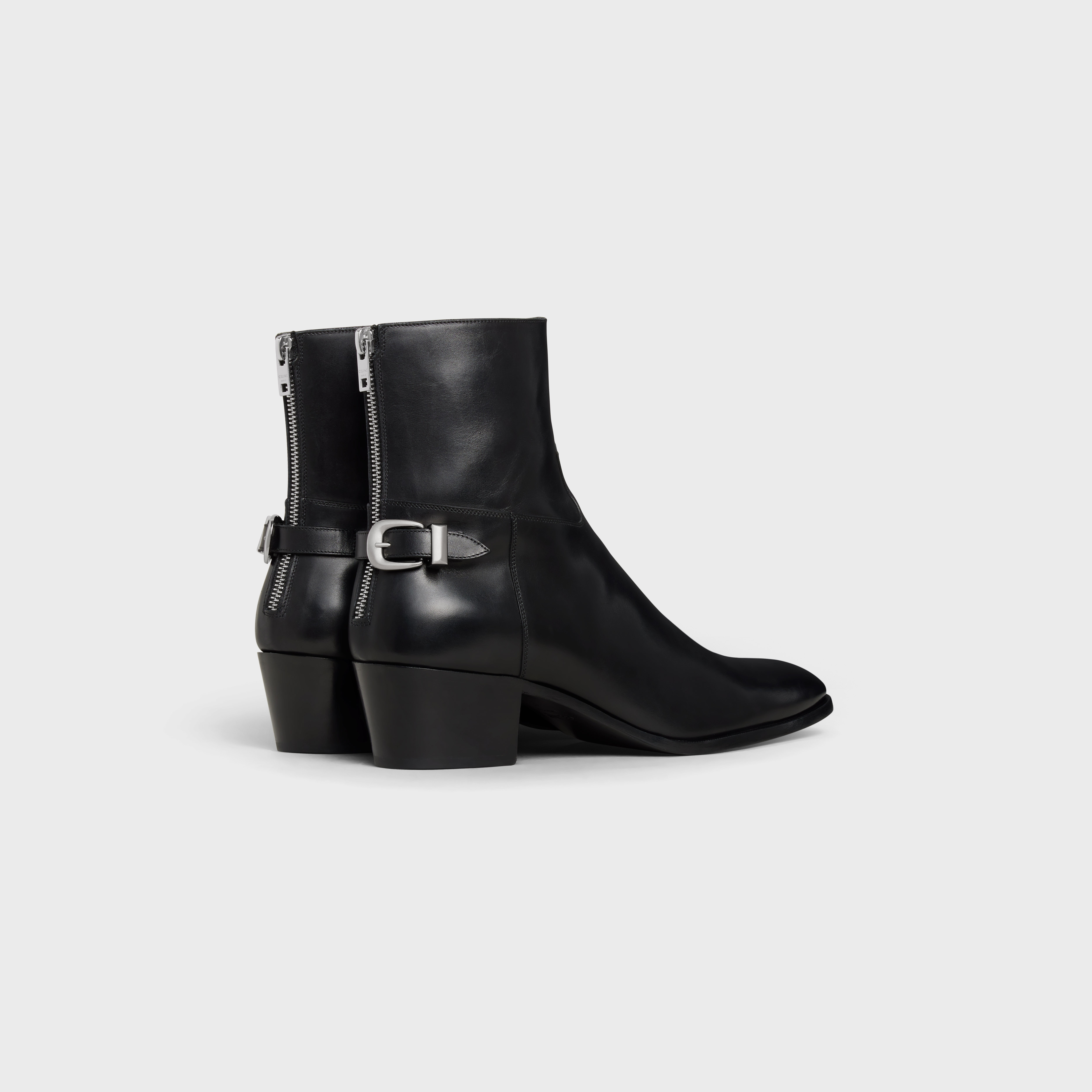
- BACK BUCKLE ZIPPED ISAAC BOOT IN SHINY CALFSKIN - BLACK